https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Reality
@ Scientific.NET Scientific Publisher provides high-demand content focused on Materials Science and Engineering – Links & How does Machine learning affect Industrial Robotics @ Breaking: Possible Signs of Life on Mars Confirmed @ Telehealth follow-ups aid communication between patients, physicians @ This wristband tells you what food to buy based on your DNA @ Protecting Teens’ Mental Health Is A Wise Investment
https://www.scientific.net/?fbclid=IwAR0CKUAFEDVjzUUpeNsPGPJIL14d_2uzUjQrjkyrOx-Vn0pjfv3oKXyqEM8
https://www.linkedin.com/company/scientificnet/ https://www.techywriters.com/how-does-machine-learning-affect-industrial-robotics/?fbclid=IwAR1aFZfBZooPB0W3xT8gLkIJBGPCuJGYV5nwNxAWHparnsfvOGLvMbg-HXE
https://www.researchgate.net/post/What_is_the_best_animal_model_for_Alzheimers_disease
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Simulated_reality https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Simulation_hypothesis https://now.northropgrumman.com/is-our-entire-universe-just-a-simulated-reality/ https://bigthink.com/mind-brain/are-we-living-in-a-simulation http://www.google.com http://www.facebook.com http://www.forbes.com http://www.linkedin.com http://www.yahoo.com http://www.harvard.edu http://www.nasa.gov http://www.nobelprize.org http://www.mit.edu http://www.stanford.edu http://www.ucla.edu http://www.caltech.edu
https://www.facebook.com/groups/Is.Reality.A.Simulation.Anthology/ https://www.nbcnews.com/mach/science/what-simulation-hypothesis-why-some-think-life-simulated-reality-ncna913926 https://www.vulture.com/2019/02/15-irrefutable-reasons-we-might-be-living-in-a-simulation.html https://www.vox.com/future-perfect/2019/4/10/18275618/simulation-hypothesis-matrix-rizwan-virk
https://www.theguardian.com/technology/2016/oct/11/simulated-world-elon-musk-the-matrix https://www.nbcnews.com/mach/science/what-simulation-hypothesis-why-some-think-life-simulated-reality-ncna913926 http://www.wikipedia.org
http://www.famerp.br http://www.uftm.edu https://techgrabyte.com/elon-musks-ai-1-billion-microsoft/?fbclid=IwAR0N_ikVOLCsVVzOzslZ82HA3DrSxrbjXv1V2EXt4s96PbitLS4tvmJ65YY
https://www.facebook.com/groups/EschatonOmegaHypercomputer/










Techgrabyte
Machine Learning Deep Learning Artificial Intelligence

Elon Musk’s AI project to replicate the human brain receives $1 billion from Microsoft
- 1.17kShares
Microsoft and Elon Musk’s OpenAI are teaming up to improve the way AI works and use to solve real-world problems. Microsoft has agreed to invest $1 billion in a partnership with the research group OpenAI.
OpenAI said the investment would go towards its efforts of building artificial general intelligence (AGI) that can rival and surpass the cognitive capabilities of humans.
This partnership will aim to get computers to learn new skills and complete varied tasks like humans can. That’s a contrast to existing A.I, which can learn specific jobs, such as understanding images and patterns but can’t tackle different problems on its own.
“The creation of AGI will be the most important technological development in human history, with the potential to shape the trajectory of humanity,” said OpenAI CEO Sam Altman.
“Our mission is to ensure that AGI technology benefits all of humanity, and we’re working with Microsoft to build the supercomputing foundation on which we’ll build AGI.”
The two tech firm is going to create a new Azure supercomputing tech in the AI field. Microsoft is going to be OpenAI’s exclusive cloud computing partner.
The companies said that they will build a hardware and software platform of “unprecedented scale” within Microsoft’s cloud service provider Azure that will train and run increasingly advanced AI models.
“By bringing together, OpenAI’s breakthrough technology with new Azure AI supercomputing technologies, our ambition is to democratize AI, while always keeping AI safety front and center so everyone can benefit,” said Microsoft CEO Satya Nadella in the statement.
“Modern AI systems work well for the specific problem on which they’ve been trained, but getting AI systems to help address some of the hardest problems facing the world today will require generalization and deep mastery of multiple AI technologies,” the companies wrote in a press release announcing the partnership.
OpenAI said Microsoft was also going to be its preferred commercialization partner, rather than making its own product. The company also said it was licensing some of its “pre-AGI technologies.” The two companies are collaborating on “shared principles on ethics and trust,” according to the release.
Other OpenAI investors include the charitable foundation of LinkedIn co-founder Reid Hoffman and venture capital firm Khosla Ventures. Other Silicon Valley entrepreneurs who started OpenAI include Hoffman and Altman, co-founder and former president of startup incubator Y Combinator.
OpenAI, co-founded in 2015 by Musk and other prominent Silicon Valley investors, focuses mainly on artificial general intelligence, which could perform any tasks that humans are capable of, different from existing AI that can do only what people trained them for.
The startup has already achieved a number of AI milestones, most notably beating the world’s best human players at the video game Dota 2, but hopes its technology can one day help address climate change and other major challenges facing the planet.
Microsoft also recently announced a partnership with AT&T that would let the communications giant use Microsoft’s Azure cloud system for its computing purposes.
At&T will also be able to use Microsoft 365 for its workers. Under the terms of the deal, the two companies will collaborate on what’s called edge computing, which means that Microsoft technology will be incorporated in AT&T’s forthcoming 5G network.
They will collaborate on speeding up data passage for certain applications, like air traffic for drones. Microsoft will become AT&T’s “preferred” cloud company, and the move will help it gain ground on rivals like Amazon, which is currently the largest cloud provider.
Customers of cloud services run software managed by the providers, in data centers. John Donovan, chief executive of AT&T Communications, said the deal represents a total shift in how the company used to operate, and that it will be “public cloud-first,” and rely on data centers to power the business.
More in AI
New AI Detects Guns, Identifies Shooters And Alert Law Enforcement
The US Army Is Developing AI Missiles That Find Their Own Targets
100% Accurate Artificial Intelligence Detects Heart Failure From Single Heartbeat
How Father Of AI, Sir Alan Turing Is Connected To INDIA !!!
You May Also Like

Understanding Machine Learning: From Theory to Algorithms

Japanese Researchers Build An AI That Identifies Early-Stage Of Stomach Cancer

MIT Researchers Created AI Model To Make Brain Cancer Treatment Less Toxic
Leave a Reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Comment
Name *
Email *
Website
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
News

Elon Musk’s AI project to replicate the human brain receives $1 billion from Microsoft
- 1.17kShares
Microsoft and Elon Musk’s OpenAI are teaming up to improve the way AI works and use to solve real-world problems.

The Seven Legit Deep Learning Courses To Become DL Expert (Free)

New AI Detects Guns, Identifies Shooters And Alert Law Enforcement

The New AI Toilets Will Scan Your Poop To Diagnose Your Ailments
About Us
Hii ! This is Navin
Techgrabyte is a education website whose area of work is Artificial Intelligence, Machine Learning and Deep Learning.
Join our Newsletter, to get daily update.
“AI is the new electricity”
About UsCOPYRIGHT © 2019 TechgraByte | All RIGHT RESERVED BY NAVIN BONDADE
Simulated reality
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopediaJump to navigationJump to searchNot to be confused with Virtual reality.
| This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed. Find sources: “Simulated reality” – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (August 2017) (Learn how and when to remove this template message) |
Simulated reality is the hypothesis that reality could be simulated—for example by quantum computer simulation—to a degree indistinguishable from “true” reality. It could contain conscious minds which may or may not be fully aware that they are living inside a simulation. This is quite different from the current, technologically achievable concept of virtual reality. Virtual reality is easily distinguished from the experience of actuality; participants are never in doubt about the nature of what they experience. Simulated reality, by contrast, would be hard or impossible to separate from “true” reality. There has been much debate over this topic, ranging from philosophical discourse to practical applications in computing.
Contents
- 1Arguments
- 2Philosophical and religious implications
- 3In fiction
- 4See also
- 5References
- 6Bibliography
- 7External links
Arguments[edit]
Simulation argument[edit]
Main article: Simulation hypothesis
A version of the simulation hypothesis was first theorised as a part of a philosophical argument on the part of René Descartes, and later by Hans Moravec.[1][2][3] The philosopher Nick Bostrom developed an expanded argument examining the probability of our reality being a simulation.[4] His argument states that at least one of the following statements is very likely to be true:1. Human civilization or a comparable civilization is unlikely to reach a level of technological maturity capable of producing simulated realities or such simulations are physically impossible to construct.[4]2. A comparable civilization reaching aforementioned technological status will likely not produce a significant number of simulated realities (one that might push the probable existence of digital entities beyond the probable number of “real” entities in a Universe) for any of a number of reasons, such as diversion of computational processing power for other tasks, ethical considerations of holding entities captive in simulated realities, etc.[4]3. Any entities with our general set of experiences are almost certainly living in a simulation.[4]4. We are living in a reality in which posthumans have not developed yet and we are actually living in reality.[4]
Bostrom’s argument rests on the premise that given sufficiently advanced technology, it is possible to represent the populated surface of the Earth without recourse to digital physics; that the qualia experienced by a simulated consciousness are comparable or equivalent to those of a naturally occurring human consciousness, and that one or more levels of simulation within simulations would be feasible given only a modest expenditure of computational resources in the real world.[4]
If one assumes first that humans will not be destroyed nor destroy themselves before developing such a technology, and that human descendants will have no overriding legal restrictions or moral compunctions against simulating biospheres or their own historical biosphere, then, Bostrom argues, it would be unreasonable to count ourselves among the small minority of genuine organisms who, sooner or later, will be vastly outnumbered by artificial simulations.[4]
Epistemologically, it is not impossible to tell whether we are living in a simulation. For example, Bostrom suggests that a window could pop up saying: “You are living in a simulation. Click here for more information.” However, imperfections in a simulated environment might be difficult for the native inhabitants to identify and for purposes of authenticity, even the simulated memory of a blatant revelation might be purged programmatically. Nonetheless, should any evidence come to light, either for or against the skeptical hypothesis, it would radically alter the aforementioned probability.[4]
Computationalism[edit]
Main articles: Computationalism and Mathematical universe hypothesis
Computationalism is a philosophy of mind theory stating that cognition is a form of computation. It is relevant to the Simulation hypothesis in that it illustrates how a simulation could contain conscious subjects, as required by a “virtual people” simulation. For example, it is well known that physical systems can be simulated to some degree of accuracy. If computationalism is correct and if there is no problem in generating artificial consciousness or cognition, it would establish the theoretical possibility of a simulated reality. Nevertheless, the relationship between cognition and phenomenal qualia of consciousness is disputed. It is possible that consciousness requires a vital substrate that a computer cannot provide and that simulated people, while behaving appropriately, would be philosophical zombies. This would undermine Nick Bostrom‘s simulation argument; we cannot be a simulated consciousness, if consciousness, as we know it, cannot be simulated. The skeptical hypothesis remains intact, however, and we could still be envatted brains, existing as conscious beings within a simulated environment, even if consciousness cannot be simulated. It has been suggested that whereas virtual reality would enable a participant to experience only three senses (sight, sound and optionally smell), simulated reality would enable all five (including taste and touch).[citation needed]
Some theorists[5][6] have argued that if the “consciousness-is-computation” version of computationalism and mathematical realism (or radical mathematical Platonism)[7] are true then consciousnesses is computation, which in principle is platform independent and thus admits of simulation. This argument states that a “Platonic realm” or ultimate ensemble would contain every algorithm, including those which implement consciousness. Hans Moravec has explored the simulation hypothesis and has argued for a kind of mathematical Platonism according to which every object (including, for example, a stone) can be regarded as implementing every possible computation.[1]
Dreaming[edit]
Further information: Dream argument
A dream could be considered a type of simulation capable of fooling someone who is asleep. As a result, the “dream hypothesis” cannot be ruled out, although it has been argued that common sense and considerations of simplicity rule against it.[8] One of the first philosophers to question the distinction between reality and dreams was Zhuangzi, a Chinese philosopher from the 4th century BC. He phrased the problem as the well-known “Butterfly Dream,” which went as follows:
Once Zhuangzi dreamt he was a butterfly, a butterfly flitting and fluttering around, happy with himself and doing as he pleased. He didn’t know he was Zhuangzi. Suddenly he woke up and there he was, solid and unmistakable Zhuangzi. But he didn’t know if he was Zhuangzi who had dreamt he was a butterfly or a butterfly dreaming he was Zhuangzi. Between Zhuangzi and a butterfly there must be some distinction! This is called the Transformation of Things. (2, tr. Burton Watson 1968:49)
The philosophical underpinnings of this argument are also brought up by Descartes, who was one of the first Western philosophers to do so. In Meditations on First Philosophy, he states “… there are no certain indications by which we may clearly distinguish wakefulness from sleep”,[9] and goes on to conclude that “It is possible that I am dreaming right now and that all of my perceptions are false”.[9]
Chalmers (2003) discusses the dream hypothesis and notes that this comes in two distinct forms:
- that he is currently dreaming, in which case many of his beliefs about the world are incorrect;
- that he has always been dreaming, in which case the objects he perceives actually exist, albeit in his imagination.[10]
Both the dream argument and the simulation hypothesis can be regarded as skeptical hypotheses; however in raising these doubts, just as Descartes noted that his own thinking led him to be convinced of his own existence, the existence of the argument itself is testament to the possibility of its own truth. Another state of mind in which some argue an individual’s perceptions have no physical basis in the real world is called psychosis though psychosis may have a physical basis in the real world and explanations vary.
The dream hypothesis is also used to develop other philosophical concepts, such as Valberg’s personal horizon: what this world would be internal to if this were all a dream.[11]
Existence of simulated reality unprovable in any concrete sense[edit]
Known as the idea of Nested Simulations: the existence of simulated reality is seen to be unprovable in any concrete sense as there is an infinite regress problem with the argument: any evidence that is directly observed could be another simulation itself.
Even if we are a simulated reality, there is no way to be sure the beings running the simulation are not themselves a simulation and the operators of that simulation are not a simulation.[12]
“Recursive simulation involves a simulation or an entity in the simulation, creating another instance of the same simulation, running it and using its results” (Pooch and Sullivan 2000).[13]
In August 2019, philosopher Preston Greene suggested that it may be best not to find out if we’re living in a computer simulation since, if it were found to be true, such knowing may end the simulation.[14]
Philosophical and religious implications[edit]
Some philosophers and authors (Nick Bostrom‘s “Are You Living In a Computer Simulation?”, Jean Baudrillard‘s “Simulacra and Simulation”, Iurii Vovchenko’s “Answers in Simulation”[15]) tried to address the implications of the simulated reality on mankind’s way of life and future. Simulated reality has significant implications to the philosophical questions such as the questions of existence of gods, meaning of life etc. There are attempts to link religion to the simulated reality.[16]
In fiction[edit]
Main article: Simulated reality in fiction
Simulated reality in fiction has been explored by many authors, game designers and film directors.
See also[edit]
- Artificial life
- Artificial society
- Augmented reality
- Boltzmann brain
- Computational sociology
- Consensus reality
- Digital philosophy
- Digital physics
- Hyperreality
- Margolus–Levitin theorem
- Maya (religion)
- Metaverse
- Mind uploading
- OpenWorm, project to simulate the roundworm Caenorhabditis elegans.
- Philosophy of information
- Simulation hypothesis
- Social simulation
- Theory of knowledge
- Tipler’s “Omega point”
- Virtual reality simulator
- Virtual worlds
Major contributing thinkers[edit]
- Nick Bostrom and his simulation argument
- René Descartes (1596–1650) and his Evil Demon, sometimes also called his ‘Evil Genius’[17]
- George Berkeley (1685–1753) and his “immaterialism” (later referred to as subjective idealism by others)[citation needed]
- Plato (424/423 BC – 348/347 BC) and his Allegory of the Cave
- Zhuangzi (around the 4th century BCE) and his Chinese Butterfly Dream
References[edit]
- ^ Jump up to:a b Moravec, Hans, Simulation, Consciousness, Existence
- ^ Moravec, Hans, Platt, Charles Superhumanism
- ^ Moravec, Hans Pigs in Cyberspace
- ^ Jump up to:a b c d e f g h Bostrom, Nick (2003). “Are You Living in a Computer Simulation?”. Philosophical Quarterly. 53 (211): 243–255.
- ^ Bruno Marchal
- ^ Russel Standish
- ^ Hut, P.; Alford, M.; Tegmark, M. (2006). “On Math, Matter and Mind”. Foundations of Physics. 36 (6): 765–794. arXiv:physics/0510188. Bibcode:2006FoPh…36..765H. doi:10.1007/s10701-006-9048-x.
- ^ “There is no logical impossibility in the supposition that the whole of life is a dream, in which we ourselves create all the objects that come before us. But although this is not logically impossible, there is no reason whatever to suppose that it is true; and it is, in fact, a less simple hypothesis, viewed as a means of accounting for the facts of our own life, than the common-sense hypothesis that there really are objects independent of us, whose action on us causes our sensations.” Bertrand Russell, The Problems of Philosophy
- ^ Jump up to:a b René Descartes, Meditations on the First Philosophy, from Descartes, The Philosophical Works of Descartes, trans. Elizabeth S. Haldane and G.R.T. Ross (Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 1911 – reprinted with corrections 1931), Volume I, 145-46.
- ^ Chalmers, J., The Matrix as Metaphysics, Department of Philosophy, University of Arizona
- ^ Valberg, J.J. (2007). Dream, Death, and the Self. Princeton University Press. ISBN 9780691128597.
- ^ Bostrom, Nick (2009). “The Simulation Argument: Some Explanations” (PDF). If each first-level ancestor-simulation run by the non-Sims requires more resources (because they contain within themselves additional second-level ancestor-simulations run by the Sims), the non-Sims might well respond by producing fewer first-level ancestor-simulations. Conversely, the cheaper it is for the non-Sims to run a simulation, the more simulations they may run. It is therefore unclear whether the total number of ancestor-simulations would be greater if Sims run ancestor-simulations than if they do not.
- ^ Pooch, U.W.; Sullivan, F.J. (2000). Recursive simulation to aid models of decisionmaking. Simulation Conference. 1 (Winter ed.). p. 958. doi:10.1109/WSC.2000.899898. ISBN 978-0-7803-6579-7.
- ^ Greene, Preston (10 August 2019). “Are We Living in a Computer Simulation? Let’s Not Find Out – Experimental findings will be either boring or extremely dangerous”. The New York Times. Retrieved 11 August 2019.
- ^ Answers In Simulation [1]
- ^ Simulation Religion [2]
- ^ Chalmers, David (2005). “The Matrix as Metaphysics”. In C. Grau (ed.). Philosophers Explore the Matrix. Oxford University Press. pp. 157–158. ISBN 9780195181067. LCCN 2004059977. Evil Genius Hypothesis: I have a disembodied mind and an evil genius is feeding me sensory inputs to give the appearance of an external world. This is René Descartes’s classical skeptical hypothesis… Dream Hypothesis: I am now and have always been dreaming. Descartes raised the question: how do you know that you are not currently dreaming? Morpheus raises a similar question: ‘Have you ever had a dream, Neo, that you were so sure was real. What if you were unable to wake from that dream? How would you know the difference between the dream world and the real world?’… I think this case is analogous to the Evil Genius Hypothesis: it’s just that the role of the “evil genius” is played by a part of my own cognitive system! If my dream-generating system simulates all of space-time, we have something like the original Matrix Hypothesis. p.22
Bibliography[edit]
- Copleston, Frederick (1993) [1946]. “XIX Theory of Knowledge”. A History of Philosophy, Volume I: Greece and Rome. New York: Image Books (Doubleday). p. 160. ISBN 978-0-385-46843-5.
- Copleston, Frederick (1994) [1960]. “II Descartes (I)”. A History of Philosophy, Volume IV: Modern Philosophy. New York: Image Books (Doubleday). p. 86. ISBN 978-0-385-47041-4.
- Deutsch, David (1997). The Fabric of Reality. London: Penguin Science (Allen Lane). ISBN 978-0-14-014690-5.
- Lloyd, Seth (2006). Programming the Universe: A Quantum Computer Scientist Takes On the Cosmos. Knopf. ISBN 978-1-4000-4092-6.
- Tipler, Frank (1994). The Physics of Immortality. Doubleday. ISBN 978-0-385-46799-5.
- Lem, Stanislaw (1964). Summa Technologiae. ISBN 978-3-518-37178-7.
External links[edit]
https://simulation-argument.tumblr.com
- Software architecture
- Concepts in epistemology
- Metaphysics
- Science fiction themes
- Philosophical arguments
- Thought experiments
- Internalism and externalism
- Philosophy of mind
- Hyperreality
- Mixed reality
- Reality by type
Navigation menu
- Not logged in
- Talk
- Contributions
- Create account
- Log in
Search
Interaction
Tools
- What links here
- Related changes
- Upload file
- Special pages
- Permanent link
- Page information
- Wikidata item
- Cite this page
In other projects
Print/export
Languages
- This page was last edited on 21 September 2019, at 21:27 (UTC).
- Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License; additional terms may apply. By using this site, you agree to the Terms of Use and Privacy Policy. Wikipedia® is a registered trademark of the Wikimedia Foundation, Inc., a non-profit organization.
Simulation hypothesis
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopediaJump to navigationJump to search
The simulation hypothesis or simulation theory proposes that all of reality, including the Earth and the universe, is in fact an artificial simulation, most likely a computer simulation. Some versions rely on the development of a simulated reality, a proposed technology that would seem realistic enough to convince its inhabitants the simulation was real. The hypothesis has been a central plot device of many science fiction stories and films.
Contents
- 1Origins
- 2Simulation hypothesis
- 3Consequences of living in a simulation
- 4Testing the hypothesis physically
- 5Other uses of the simulation hypothesis in philosophy
- 6In popular culture
- 7See also
- 8References
- 9Further reading
- 10External links
Origins[edit]
There is a long philosophical and scientific history to the underlying thesis that reality is an illusion. This skeptical hypothesis can be traced back to antiquity; for example, to the “Butterfly Dream” of Zhuangzi,[1] or the Indian philosophy of Maya. A version of the hypothesis was also theorised as a part of a philosophical argument by René Descartes.
Simulation hypothesis[edit]
Nick Bostrom’s premise:
Many works of science fiction as well as some forecasts by serious technologists and futurologists predict that enormous amounts of computing power will be available in the future. Let us suppose for a moment that these predictions are correct. One thing that later generations might do with their super-powerful computers is run detailed simulations of their forebears or of people like their forebears. Because their computers would be so powerful, they could run a great many such simulations. Suppose that these simulated people are conscious (as they would be if the simulations were sufficiently fine-grained and if a certain quite widely accepted position in the philosophy of mind is correct). Then it could be the case that the vast majority of minds like ours do not belong to the original race but rather to people simulated by the advanced descendants of an original race.
Nick Bostrom’s conclusion:

Nick Bostrom in 2014
It is then possible to argue that, if this were the case, we would be rational to think that we are likely among the simulated minds rather than among the original biological ones.
Therefore, if we don’t think that we are currently living in a computer simulation, we are not entitled to believe that we will have descendants who will run lots of such simulations of their forebears.— Nick Bostrom, Are you living in a computer simulation?, 2003[2]
Ancestor simulation[edit]
In 2003, philosopher Nick Bostrom proposed a trilemma that he called “the simulation argument”. Despite the name, Bostrom’s “simulation argument” does not directly argue that we live in a simulation; instead, Bostrom’s trilemma argues that one of three unlikely-seeming propositions is almost certainly true:
- “The fraction of human-level civilizations that reach a posthuman stage (that is, one capable of running high-fidelity ancestor simulations) is very close to zero”, or
- “The fraction of posthuman civilizations that are interested in running simulations of their evolutionary history, or variations thereof, is very close to zero”, or
- “The fraction of all people with our kind of experiences that are living in a simulation is very close to one”
The trilemma points out that a technologically mature “posthuman” civilization would have enormous computing power; if even a tiny percentage of them were to run “ancestor simulations” (that is, “high-fidelity” simulations of ancestral life that would be indistinguishable from reality to the simulated ancestor), the total number of simulated ancestors, or “Sims”, in the universe (or multiverse, if it exists) would greatly exceed the total number of actual ancestors.
Bostrom goes on to use a type of anthropic reasoning to claim that, if the third proposition is the one of those three that is true, and almost all people with our kind of experiences live in simulations, then we are almost certainly living in a simulation.
Bostrom claims his argument goes beyond the classical ancient “skeptical hypothesis“, claiming that “…we have interesting empirical reasons to believe that a certain disjunctive claim about the world is true”, the third of the three disjunctive propositions being that we are almost certainly living in a simulation. Thus, Bostrom, and writers in agreement with Bostrom such as David Chalmers, argue there might be empirical reasons for the “simulation hypothesis”, and that therefore the simulation hypothesis is not a skeptical hypothesis but rather a “metaphysical hypothesis“. Bostrom states he personally sees no strong argument for which of the three trilemma propositions is the true one: “If (1) is true, then we will almost certainly go extinct before reaching posthumanity. If (2) is true, then there must be a strong convergence among the courses of advanced civilizations so that virtually none contains any individuals who desire to run ancestor-simulations and are free to do so. If (3) is true, then we almost certainly live in a simulation. In the dark forest of our current ignorance, it seems sensible to apportion one’s credence roughly evenly between (1), (2), and (3)… I note that people who hear about the simulation argument often react by saying, ‘Yes, I accept the argument, and it is obvious that it is possibility #n that obtains.’ But different people pick a different n. Some think it obvious that (1) is true, others that (2) is true, yet others that (3) is true.”
As a corollary to the trilemma, Bostrom states that “Unless we are now living in a simulation, our descendants will almost certainly never run an ancestor-simulation.”[3][4][5][6]
Criticism of Bostrom’s anthropic reasoning[edit]
Further information: Anthropic principle
Bostrom argues that if “the fraction of all people with our kind of experiences that are living in a simulation is very close to one”, then it follows that we probably live in a simulation. Some philosophers disagree, proposing that perhaps “Sims” do not have conscious experiences the same way that unsimulated humans do, or that it can otherwise be self-evident to a human that they are a human rather than a Sim.[4][7] Philosopher Barry Dainton modifies Bostrom’s trilemma by substituting “neural ancestor simulations” (ranging from literal brains in a vat, to far-future humans with induced high-fidelity hallucinations that they are their own distant ancestors) for Bostrom’s “ancestor simulations”, on the grounds that every philosophical school of thought can agree that sufficiently high-tech neural ancestor simulation experiences would be indistinguishable from non-simulated experiences. Even if high-fidelity computer Sims are never conscious, Dainton’s reasoning leads to the following conclusion: either the fraction of human-level civilizations that reach a posthuman stage and are able and willing to run large numbers of neural ancestor simulations is close to zero, or we are in some kind of (possibly neural) ancestor simulation.[8]
Some scholars categorically reject or are uninterested in anthropic reasoning, dismissing it as “merely philosophical”, unfalsifiable, or inherently unscientific.[4]
Some critics reject the block universe view of time that Bostrom implicitly accepts and propose that we could be in the first generation, such that all the simulated people that will one day be created don’t yet exist.[4]
The cosmologist Sean M. Carroll argues that the simulation hypothesis leads to a contradiction: if a civilization is capable of performing simulations, then it will likely perform many simulations, which implies that we are most likely at the lowest level of simulation (from which point one’s impression will be that it is impossible to perform a simulation), which contradicts the arguer’s assumption that advanced civilizations can most likely perform simulations.[9]
Arguments, within the trilemma, against the simulation hypothesis[edit]
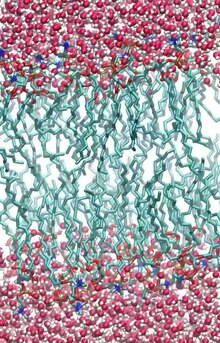
Simulation down to molecular level of very small sample of matter
Some scholars accept the trilemma, and argue that the first or second of the propositions are true, and that the third proposition (the proposition that we live in a simulation) is false. Physicist Paul Davies deploys Bostrom’s trilemma as part of one possible argument against a near-infinite multiverse. This argument runs as follows: if there were a near-infinite multiverse, there would be posthuman civilizations running ancestor simulations, and therefore we would come to the untenable and scientifically self-defeating conclusion that we live in a simulation; therefore, by reductio ad absurdum, existing multiverse theories are likely false. (Unlike Bostrom and Chalmers, Davies (among others) considers the simulation hypothesis to be self-defeating.)[4][10]
Some point out that there is currently no proof of technology which would facilitate the existence of sufficiently high-fidelity ancestor simulation. Additionally, there is no proof that it is physically possible or feasible for a posthuman civilization to create such a simulation, and therefore for the present, the first proposition must be true.[4] Additionally there are limits of computation[2].
Consequences of living in a simulation[edit]
Economist Robin Hanson argues a self-interested high-fidelity Sim should strive to be entertaining and praiseworthy in order to avoid being turned off or being shunted into a non-conscious low-fidelity part of the simulation. Hanson additionally speculates that someone who is aware that he might be a Sim might care less about others and live more for today: “your motivation to save for retirement, or to help the poor in Ethiopia, might be muted by realizing that in your simulation, you will never retire and there is no Ethiopia.”[11]
Testing the hypothesis physically[edit]
A long-shot method to test one type of simulation hypothesis was proposed in 2012 in a joint paper by physicists Silas R. Beane from the University of Bonn (now at the University of Washington, Seattle), and Zohreh Davoudi and Martin J. Savage from the University of Washington, Seattle.[12] Under the assumption of finite computational resources, the simulation of the universe would be performed by dividing the continuum space-time into a discrete set of points. In analogy with the mini-simulations that lattice-gauge theorists run today to build up nuclei from the underlying theory of strong interactions (known as quantum chromodynamics), several observational consequences of a grid-like space-time have been studied in their work. Among proposed signatures is an anisotropy in the distribution of ultra-high-energy cosmic rays, that, if observed, would be consistent with the simulation hypothesis according to these physicists.[13] A multitude of physical observables must be explored before any such scenario could be accepted or rejected as a theory of nature.[14] In 2017, Campbell et al. proposed several experiments aimed at testing the simulation hypothesis in their paper “On Testing the Simulation Theory”.[15] In 2018 they started a Kickstarter campaign to fund the experiments, which reached $236,590, more than the required sum of $150,000.[16]
In 2019, philosopher Preston Greene suggested that it may be best not to find out if we’re living in a simulation since, if it were found to be true, such knowing may end the simulation.[17]
Other uses of the simulation hypothesis in philosophy[edit]
Besides attempting to assess whether the simulation hypothesis is true or false, philosophers have also used it to illustrate other philosophical problems, especially in metaphysics and epistemology. David Chalmers has argued that simulated beings might wonder whether their mental lives are governed by the physics of their environment, when in fact these mental lives are simulated separately (and are thus, in fact, not governed by the simulated physics).[18] They might eventually find that their thoughts fail to be physically caused. Chalmers argues that this means that Cartesian dualism is not necessarily as problematic of a philosophical view as is commonly supposed, though he does not endorse it.
Similarly, Vincent Conitzer has used the following computer simulation scenarios to illuminate further facts—facts that do not follow logically from the physical facts—about qualia (what it is like to have specific experiences), indexicality (what time it is now and who I am), and personal identity.[19] Imagine a person in the real world who is observing a simulated world on a screen, from the perspective of one of the simulated agents in it. The person observing knows that besides the code responsible for the physics of the simulation, there must be additional code that determines in which colors the simulation is displayed on the screen, and which agent’s perspective is displayed. (These questions are related to the inverted spectrum scenario and whether there are further facts about personal identity.) That is, the person can conclude that the facts about the physics of the simulation (which are completely captured by the code governing the physics) do not fully determine her experience by themselves. But then, Conitzer argues, imagine someone who has become so engrossed in the simulation that she has forgotten that it is a simulation she is watching. Could she not still reach the same conclusion? And if so, can we not conclude the same in our own daily lives?
In popular culture[edit]
Science fiction themes[edit]
Main articles: Simulated reality in fiction and Simulated consciousness (science fiction)
Science fiction has highlighted themes such as virtual reality, artificial intelligence and computer gaming for more than fifty years. Simulacron-3 (1964) by Daniel F. Galouye (alternative title: Counterfeit World) tells the story of a virtual city developed as a computer simulation for market research purposes, in which the simulated inhabitants possess consciousness; all but one of the inhabitants are unaware of the true nature of their world. The book was made into a German made-for-TV film called World on a Wire (1973) directed by Rainer Werner Fassbinder. The movie The Thirteenth Floor (1999) was also loosely based on this book. “We Can Remember It for You Wholesale” is a short story by American writer Philip K. Dick, first published in The Magazine of Fantasy & Science Fiction in April 1966, and was the basis for Total Recall (1990 film) and Total Recall (2012 film). In Overdrawn at the Memory Bank, a 1983 television movie, the main character pays to have his mind connected to a simulation. More recently, the same theme was repeated in the 1999 film The Matrix, which depicted a world in which artificially intelligent robots enslaved humanity within a simulation set in the contemporary world. The 2012 play World of Wires was partially inspired by the Bostrom essay on the simulation hypothesis.[20] In the episode “Extremis” (broadcast on 20 May 2017 on BBC One) of the science fiction series Doctor Who, aliens called “The Monks” plan an invasion of Earth by running and studying a holographic simulation of Earth with conscious inhabitants. When the virtual Doctor finds out about the simulation he sends an email about the simulation to his real self so that the real Doctor can save the world. In the first season of Rick and Morty, a science-fiction animated comedy, the episode “M. Night Shaym-Aliens!” aliens trap the lead role (Rick) in a simulated reality in order to trick him into revealing his formula for concentrated dark matter. In the game Xenoblade Chronicles, it is revealed that the whole world of the gods Bionis and Mechonis was a simulation run by Alvis, the administrative computer of a phase transition experiment facility (heavily implied to be “Ontos” in Xenoblade Chronicles 2) after Klaus destroyed the universe in a multi-verse experiment. Simulation Theory is also the name of the eighth album by British alternative band Muse, released on 9 November 2018. “Answers In Simulation” [21] by Iurii Vovchenko was released in 2019. This book addresses the subject of simulation from another angle. The author makes a statement “OK, we live in simulation” and then asks a question “What’s next for us in that case?”
See also[edit]
- Avatamsaka Sutra – a Mahayana Buddhist text describing a cosmos of infinite realms
- Digital physics
- Holographic principle
- Mathematical universe hypothesis
- Simulated reality
References[edit]
- ^ “You’re living in a computer simulation, and math proves it”. Gizmodo. Retrieved 29 October 2016.
- ^ Jump up to:a b Bostrom, Nick (2003). “Are You Living in a Computer Simulation?”. Philosophical Quarterly. 53(211): 243–255.
- ^ Bostrom, N., 2003, Are You Living in a Simulation?, Philosophical Quarterly (2003), Vol. 53, No. 211, pp. 243-255.
- ^ Jump up to:a b c d e f The Simulation Argument Website FAQ
- ^ The Simulation Argument: Why the Probability that You Are Living in a Matrix is Quite High, Nick Bostrom, Professor of Philosophy at Oxford University, 2003
- ^ Davis J. Chalmers The Matrix as Metaphysics Dept of Philosophy, U. o Arizona; paper written for the philosophy section of The Matrix website.
- ^ Brian Weatherson. “Are you a sim?” The Philosophical Quarterly 53.212 (2003): 425-431.
- ^ Dainton, Barry. “On singularities and simulations.” Journal of Consciousness Studies 19.1 (2012): 42.
- ^ http://www.preposterousuniverse.com/blog/2016/08/22/maybe-we-do-not-live-in-a-simulation-the-resolution-conundrum/
- ^ Davies, Paul, Charles William. “Multiverse cosmological models.” Modern Physics Letters A 19.10 (2004): 727-743.
- ^ Robin Hanson. “How to live in a simulation.” Journal of Evolution and Technology 7.1 (2001).
- ^ Beane, Silas; Zohreh Davoudi; Martin J. Savage (9 November 2012). “Constraints on the Universe as a Numerical Simulation”. arXiv:1210.1847. Bibcode:2014EPJA…50..148B. doi:10.1140/epja/i2014-14148-0. Lay summary – The Physics arXiv Blog (October 10, 2012). ABSTRACT Observable consequences of the hypothesis that the observed universe is a numerical simulation performed on a cubic space-time lattice or grid are explored. The simulation scenario is first motivated by extrapolating current trends in computational resource requirements for lattice QCD into the future. Using the historical development of lattice gauge theory technology as a guide, we assume that our universe is an early numerical simulation with unimproved Wilson fermion discretization and investigate potentially-observable consequences. Among the observables that are considered are the muon g-2 and the current differences between determinations of alpha, but the most stringent bound on the inverse lattice spacing of the universe, b−1 > ~ 10^11 GeV, is derived from the high-energy cut off of the cosmic ray spectrum. The numerical simulation scenario could reveal itself in the distributions of the highest energy cosmic rays exhibiting a degree of rotational symmetry breaking that reflects the structure of the underlying lattice.
- ^ Moskowitz, Clara. “Are We Living in a Computer Simulation?”.
- ^ “Physics Home”. http://www.phys.washington.edu.
- ^ Campbell, Tom; Owhadi, Houman; Sauvageau, Joe; Watkinson, David (June 17, 2017). “On Testing the Simulation Theory”. International Journal of Quantum Foundations. 3 (3): 78–99.
- ^ “Do we live in a Virtual Reality?”. Kickstarter. Retrieved 2018-09-15.
- ^ Greene, Preston (10 August 2019). “Are We Living in a Computer Simulation? Let’s Not Find Out – Experimental findings will be either boring or extremely dangerous”. The New York Times. Retrieved 11 August 2019.
- ^ Chalmers, David (January 1990). “How Cartesian Dualism Might Have Been True”.
- ^ Conitzer, Vincent (2018). “A Puzzle about Further Facts”. Erkenntnis. arXiv:1802.01161. doi:10.1007/s10670-018-9979-6.
- ^ Brantley, Ben (January 16, 2012). “‘World of Wires’ at the Kitchen — Review”. The New York Times.
- ^ “Answers In Simulation”[1]
Further reading[edit]
- “Are We Living in a Simulation?” BBC Focus magazine, March 2013, pages 43–45. Interview with physicist Silas Beane of the University of Bonn discussing a proposed test for simulated reality evidence. Three pages, three photos, including one of Beane and a computer-generated scene from the film The Matrix. Publisher: Immediate Media Company, Bristol, UK.
- “Do We Live in the Matrix?” by Zeeya Merali, Discover, December 2013, pages 24–25. Subtitle: “Physicists have proposed tests to reveal whether we are part of a giant computer simulation.”
- Tom Campbell, Houman Owhadi, Joe Sauvageau, David Watkinson: On testing the simulation theory. arXiv:1703.00058.
- Conitzer, Vincent. A Puzzle about Further Facts. Open access version of article in Erkenntnis.
- Virk, Rizwan. The Simulation Hypothesis: An MIT Computer Scientist Shows Why AI, Quantum Physics, and Eastern Mystics All Agree We Are In a Video Game.
- Lev, Gid’on. Life in the Matrix. Haaretz Magazine, April 25, 2019, page 6.
- Nested Simulations Theory. Simulated Reality, How Deep Does it Go?
External links[edit]
- Are You Living In a Computer Simulation? Nick Bostrom‘s Simulation Argument webpage.
- Megaminds, abstract evolution and the consistency machine, aka how to build simulated realities
- Techniques for programming a Simulation Universe at the Planck level
- Science fiction themes
- Arguments in philosophy of mind
- Internalism and externalism
- Epistemological theories
- Metaphysical theories
- Virtual reality
- Consensus reality
- Hyperreality
- Hypotheses
- Nick Bostrom
Navigation menu
- Not logged in
- Talk
- Contributions
- Create account
- Log in
Search
Interaction
Tools
- What links here
- Related changes
- Upload file
- Special pages
- Permanent link
- Page information
- Wikidata item
- Cite this page
Print/export
Languages
- This page was last edited on 21 September 2019, at 21:14 (UTC).
- Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License; additional terms may apply. By using this site, you agree to the Terms of Use and Privacy Policy. Wikipedia® is a registered trademark of the Wikimedia Foundation, Inc., a non-profit organization.
Skip to contentTuesday, October 29, 2019Latest:
- Artificial Intelligence vs Machine Learning: The important differences between them
- Are we slaves of Artificial Intelligence? How our lifestyle is governed by Artificial Intelligence.
- The Food Printing Technology Revolution: How Do 3D Food Printers Change Our Food?
- How does Machine learning affect Industrial Robotics
- How will Artificial Intelligence Affect the Future of Our World?

Techy Writers
Peerless AI Science and Tech news.

Artificial IntelligenceNewsTech
How does Machine learning affect Industrial Robotics
2019 September, 10Wiky 1 CommentArtificial Intelligence, Business, Education, featured, Future Tech, news, smart, Tech
Artificial intelligence and machine learning involve software programs classifying data and creating decisions about things within the real world. robotics involves manipulating objects within the real world. This creates the power to manipulate the important world using a combination of machine learning and robotics.
only some of the recent developments in robotics may be attributable to developments and uses of machine learning.
Some researchers might even argue against a set definition for the robot or discussion whether a definition may be relative or dependent upon the context of a situation, like the concept of ‘privacy’, this could be a better improved as more and more rules and laws are created around their use in variable contexts. There’s additionally some discussion on whether the term robot includes innovations like autonomous vehicles, drones, and different similar machines. I argue that these kinds of machines are a category of the mobile robot.
There are four areas of robotic processes that artificial intelligence and machine learning are impacting to create current applications more economical and profitable. The scope of artificial intelligence in robotics includes:
- Vision: Artificial intelligence is helping robots discover things they’ve never seen before and recognized objects with so much greater detail.
- Grasping: robots also are grasping things they’ve never seen before with Artificial intelligence and machine learning serving to them confirm the best position and orientation to know an object.
- Motion Control: machine learning helps robots with dynamic interaction and obstacle rejection to maintain productivity.
- Data analysis: Artificial intelligence and machine learning both facilitate robots to understand physical and logistic data patterns to be proactive and act accordingly.
FANUC Corporation is a leader within the Artificial intelligence and industrial robot industry. The manufacturer has been specializing in Artificial intelligence and larger connectivity in its industrial robots on various fronts. the corporation has been utilizing FANUC Intelligent Edge Link and Drive platform of commercial internet of things for purposes of producing. KUKA robotics is another leader in robot manufacturing, that implements machine learning and Artificial intelligence technology in their cooperative robots. The ensuing product is a robot which will safely work alongside people, which can be reprogrammed to permit for new tasks. this is unlike ancient industrial robots that depend on intensive coding for the performance of every task.
One of the top advantages that can simply be realized from this technology is increased productivity and uptime as a result of predictive maintenance. Integration of industrial robotics technology and AI permits robots to monitor their performance and accuracy, showing the moment maintenance is required to stop expensive downtime.
Collaborative robots usually utilize machine learning technology and Artificial intelligence. as an example, Baxter and Sawyer robots by Rethink robotics are cooperative robots that can be coded for various tasks at one time and can learn to accomplish tasks safely aboard people.
There are collaborative robots which will be coded simply by teaching them how to perform a task. The robot will then redo the task and learn the explanation for failure each time it attempts. This will be until it can accomplish a task with repeatability of a high degree.
There are various benefits of Artificial intelligence, industrial robotics, and machine learning technologies combining into one system for manufacturing production. Reduced programming time, higher productivity, and accrued uptime are some of the most effective benefits for the current manufacturers. But, Artificial intelligence and machine learning will have a transformative impact on industrial robots. whereas these technologies are still in their infancy, they’ll still push the boundaries of what’s potential with industrial robotic automation over the future.Please follow and like us:
Related

Artificial Intelligence vs Machine Learning
2019 September, 7

Everything you need to know about Artificial Intelligence
2019 June, 15

Artificial Intelligence vs Machine Learning: The important differences between them
2019 September, 8
- ← How will Artificial Intelligence Affect the Future of Our World?
- The Food Printing Technology Revolution: How Do 3D Food Printers Change Our Food? →
You May Also Like

Artificial Intelligence in Business : How Artificial Intelligence Will Transform Business

Artificial Intelligence vs Machine Learning

Are we slaves of Artificial Intelligence? How our lifestyle is governed by Artificial Intelligence.
One thought on “How does Machine learning affect Industrial Robotics”
- sirglio frei2019 October, 10 at 11:33 AMPermalinkIt is perfect time to make some plans for the future and it’s time to be happy. I’ve read this post and if I could I wish to suggest you some interesting things or suggestions. Perhaps you can write next articles referring to this article. I want to read even more things about it!Reply
Leave a Reply
Your email address will not be published.
Comment
Name
Website
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Latest Posts

Artificial IntelligenceNewsTech
Are we slaves of Artificial Intelligence? How our lifestyle is governed by Artificial Intelligence.
In less than a decade, AI has moved from a mostly arcane educational pursuit into the mainstream of business and

The Food Printing Technology Revolution: How Do 3D Food Printers Change Our Food?

How does Machine learning affect Industrial Robotics

How will Artificial Intelligence Affect the Future of Our World?
Business

The Food Printing Technology Revolution: How Do 3D Food Printers Change Our Food?
If you can get the same food at the market or even make it yourself, why waste energy into this

Intel is rumored to be releasing 10-core Comet Lake CPU for the desktop computers by 2020

The Huawei company said operating system which also goes by the name Hongmeng is not for smartphones

United States companies will be allowed to work with Huawei again, President Trump announced
Filters
AgricultureAmazonAndroidAndroid ROOTApple ProductsApple SoftwaresAppsArtificial IntelligenceBusinessDesktop Operating systemsdevicesEducationEntertainmentfeaturedFuture TechgadgetGamesGooglehacksHealthHow ToiOSiOS JailbreakingMachine Learningmilitary techMobile Operating systemsMobilesnewsPC GamingpopularProducts ReviewsReviewsSciencesmartSmartphoneSoftware ReviewsTechtipstrendingvoice assistantsWindows Softwares
Latest New from our Blog
- The Evolution of the iPhones
- What is the mac Operating system ?
- What is Jailbreaking ?? (The results of jailbreaking, How a jailbreak works ?)
- What Does an Operating Systems Do?
- What is Software ?
- What is Google Assistant?(What can Google Assistant do?)
- Which devices offer Google Assistant?
- what is the Amazon Alexa ?
- Who is Cortana ?(What is Cortana useful for?)
- What is Siri? & How Can Siri Help Me?
- What is a voice assistant?(How do voice assistants work)
- WHAT IS ROOTING?(WHY WOULD YOU ROOT)
Welcome to TechyWriters
Your number one source for all things. We’re dedicated to giving you the very best of contents, with a focus on Artificial Intelligence, new scientific discoveries, entertainment contents, tech products and new technologies in the business world.
Connect us
contact@techywriters.com
Join us
Copyright © 2019 Techy Writers. All rights reserved.
Theme: ColorMag by ThemeGrill. Powered by WordPress.

MenuContact usAbout usPrivacy Policy
Physics And Astronomy Zone
Breaking: Possible Signs of Life on Mars Confirmed
AdminApril 03, 20190Scientists have independently confirmed methane on Mars, in a possible sign of life on the planet. The gas was first spotted on the Martian surface more than a decade ago. But debate has raged about whether the detection was legitimate, as well as about where it could have come from if it is.

Now it has been independently confirmed for the first time, marking a major step forward in the hunt for the mysterious source of the gas. On Earth, methane is a key sign of life, and is emitted from biological organisms. Even if the Martian gas is coming from another process, it is still likely to be an indication that the red planet’s surface is far more active than previously thought.
In June 2013, the Curiosity rover spotted methane on the Martian surface, near the Gale Crater. The new findings come after scientists used a spectrometer on a spacecraft to observe methane in the Martian atmosphere, near the Gale Crater. They were also able to investigate the potential source of the methane, using numerical modelling and geological analysis, which suggested that it is coming from a fault near Gale Crater that is releasing it into the Martian atmosphere.
That should prove useful to scientists looking to investigate further where the methane could be coming from. Ever since methane was first detected, more than 10 years ago, debate has raged about whether it is coming from microorganisms or from geochemical reactions underground.
If it is coming from microorganisms then scientists could be able to follow the trace of gas in an attempt to discover whatever life could be hiding beneath the Martian surface. But the researchers in the new paper, titled ‘Independent confirmation of a methane spike on Mars and a source region east of Gale Crater’ and published in Nature Geoscience, note that will not be possible until its source can be found.
Scientists sent the ExoMars orbiter to the planet in 2016, in the hope that it can better understand the operation of methane on its surface and possible understand better where it is emerging from. As well as confirming the previous detection, and helping locate a possible location to search for further emissions, the new paper suggests that the methane on Mars might not be emerging in the way some expect.
Rather than coming from large emissions and being present around the whole of Mars, it might instead come out in small, short emissions from whatever process is producing it, the researchers write.Incredible $99 Smartwatch is Taking Brazil By StormXWatch|SponsoredCopycat Watch Everyone In Sao Jose Do Rio Preto Is Talking AboutXWATCH|SponsoredPoliglota de 22 anos ensina inglês em 8 semanas e vira febre na internetMétodo Inglês Rápido|SponsoredEste emagrecedor natural é o mais eficaz que você vai encontrarPhytoPower Caps|SponsoredEmpresas de ar condicionado irritadas com este novo dispositivo minúsculoCoolAir|SponsoredSusan Boyle é tão magra agora e está lindaFinanceBlvd|SponsoredCasais tiram a mesma foto juntos 50 anos depois e você vai morrer de rir!Desafio Mundial|SponsoredGabourey Sidibe Is So Skinny Now And Looks Like A ModelFinance BLVD|SponsoredFamosos que morreram sem que ninguém soubesseTherapy Joker|SponsoredEconomista confirma rumores sobre bancos brasileirosEuQueroInvestir.com|SponsoredMulher descobre botox em cápsulas e vira febre em São José Do Rio PretoDermacaps|SponsoredGenial invenção japonesa permite falar 43 idiomas instantaneamenteMUAMA Enence|SponsoredWorlds First Ever Human-Monkey Hybrid Grown In Lab In ChinaWorlds First Ever Human-Monkey Hybrid Grown In Lab In ChinaScience-andinfoNASA Openly Admits Alien Life Exists: Get Ready for DisclosureNASA Openly Admits Alien Life Exists: Get Ready for DisclosureScience-andinfoTAGS:ASTRONOMYSCIENCE
CONTACT FORM
Name
Email *
Message *
TRANSLATE

POPULAR
- The Bee Is Declared The Most Important Living Being On The Planet
- NASA Openly Admits Alien Life Exists: Get Ready for Disclosure
- Students Invent Bacteria That Eat Plastic From The Oceans And Turn It Into Water
- China Beats Nasa: China Claims It’s Already Testing ‘Impossible’ Warp Drive Technology
- Conform Proof of Life on Mars’ – shock claim after ‘Alien found’ in NASA Picture
- 10 Warning Signs The Universe Sends When You’re On The Wrong Path
- SHOCK CLAIM: Large Hadron Collider magnetic field could pull asteroids towards EarthSHOCK CLAIM: Large Hadron Collider magnetic field could pull asteroids towards Earth
- Shocking News Alien Mega structure In Universe
CATEGORIES
- ASTRONOMY(652)
- EFFECTS(508)
- LATEST TECHNOLOGY(64)
- LATEST TECHNOLOGY NEWS(315)
- NASA(1045)
- NATURE(766)
- NEW VIDEO(235)
- PHYSICS(829)
- SCIENCE(1566)
FOLLOW BY EMAIL
COMMENTS
BLOG ARCHIVE
Blog Archive November (1) October (34) September (74) August (67) July (89) June (74) May (98) April (59) March (107) February (111) January (91) December (89) November (53) October (54) September (13) August (12) July (9) April (1) March (84) February (63) January (77) December (90) November (62) October (139) September (91) August (35) July (3) April (38) March (86) February (1) October (5) September (14) August (34) July (49) June (106) May (131) April (78) March (85) February (45) January (1) March (13) February (8) July (11) June (4)
RECENT IN SPORTS
Created By Sora Templates & Blogger TemplatesWorlds First Ever Human-Monkey Hybrid Grown In Lab In ChinaWorlds First Ever Human-Monkey Hybrid Grown In Lab In ChinaRead Next StoryIncredible $99 Smartwatch is Taking Brazil By StormXWatch|SponsoredRead Next StoryPoliglota de 22 anos ensina inglês em 8 semanas e vira febre na internetMétodo Inglês Rápido|SponsoredRead Next Story

Search form
Telehealth follow-ups aid communication between patients, physiciansAnicka Slachta | November 15, 2019 | Practice Management


Following up with heart patients via computer or smartphone helped facilitate communication between patients, families and care teams in a small-scale study out of Children’s National Hospital in Washington, D.C.
The trial, led by senior author Ashraf Harahsheh, MD, a cardiologist at Children’s National, is slated for presentation at the American Heart Association’s annual Scientific Sessions in Philadelphia Nov. 17. It was a virtual visit pilot study that recruited patients with previously established hyperlipidemia, hypercholesterolemia or syncope, as well as patients who needed to discuss cardiac testing results.
“We’ve used telemedicine in pediatric cardiology for physician-to-physician communications for years at Children’s National, thanks to cardiologists like Dr. Craig Sable,” Harahsheh said in a release. Sable is the associate chief of cardiology at the hospital.
“But this is the first time we’ve really had the appropriate technology to speak directly to patients and their families in their homes instead of requiring an in-person visit.”
The team’s retrospective sample included 18 families who were open to virtual visits as a follow-up option between 2016 and 2019. Six months after their virtual visits, none of the patients reported an urgent cardiology issue.
A good portion of patients in the study—39%—had additional in-person cardiology appointments, but Harahsheh et al. said none of those appointments were the result of a deficiency in virtual visits.
“There are many more questions to be answered about how best to appropriately use technology advances that allow us to see and hear our patients without requiring them to travel a great distance,” Harahsheh said. “But my team and I were encouraged by the results of our small study, and by the anecdotal positive reviews from families who participated. We’re looking forward to determining how we can successfully and cost-effectively implement these approaches as additional options for our families to get the care they need.”
Subscribe to Cardiovascular Business News
The free daily newsletter covering the top cardiovascular headlines
By signing up you agree to our privacy policy. You can opt out anytime.




© 2019 TriMed Media Group, Inc. All Rights Reserved. | Terms of Use | Privacy Policy
We use cookies on this site to enhance your user experience
By clicking the Accept button, you agree to us doing so. More infoAccept
We use cookies to improve your experience on our website. By using our website you consent to all cookies in accordance with our updated Cookie Notice.I accept
This wristband tells you what food to buy based on your DNA

15 Nov 2019
- Douglas BroomSenior Writer, Formative Content
Predictions for 2030: What if we get things right?Read the seriesMost PopularHow to stay fit in your 60s and beyondJulie Broderick · The Conversation 14 Nov 20193 reasons why Singapore is the smartest city in the worldSharmishta Sivaramakrishnan 14 Nov 2019Alibaba hits $23 billion sales in 9 hours for Singles’ Day shoppingJosh Horwitz · Reuters 11 Nov 2019More on the agendaForum in focusThe world has entered a new era of epidemic risk. We’re responding with strength.Read more about this projectExplore context
Future of Health and HealthcareExplore the latest strategic trends, research and analysis
When an undiagnosed rare genetic disease caused his young son’s kidneys to fail, Professor Chris Toumazou vowed to find a way of uncovering hidden health risks.
The professor of biomedical engineering realised that, although his son’s condition could not have been prevented, the family could have managed his lifestyle very differently had they known about his condition.
So, he embarked on a mission to help people change their lifestyles and avoid getting sick.
Have you read?
- New AI system could diagnose breast cancer much faster than experts
- Have you heard of optoacoustic imaging? This is how it’s saving lives
- Why home DNA tests might not be as private as you think
Lifestyle, he says, has a “huge impact” on many undiagnosed conditions such as diabetes and high blood pressure. Changing behaviour could save lives.
The result of his research is a simple wristband that uses your DNA to help you make healthy choices as you shop for groceries.
By analysing the part of your genetic code determining susceptibility to nutrition-related health conditions like diabetes, DNANudge tells you which foods are best for you, and which you should avoid.
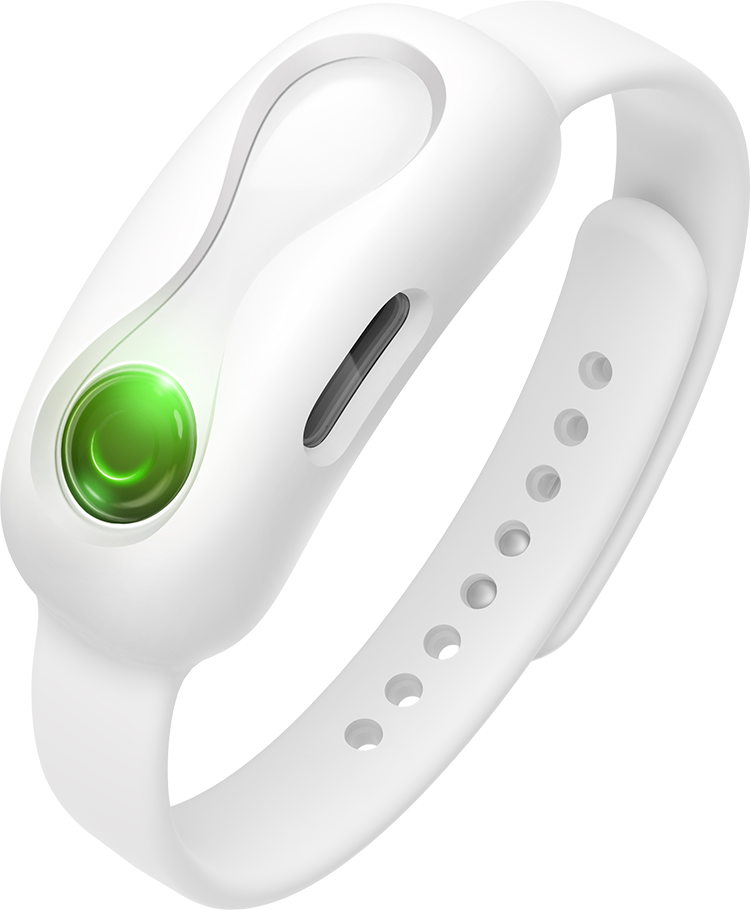

Shopping with your DNA
The wristband scans shop barcodes and shows a green light if a product is OK and red if it may be harmful in the long run. The wristband’s linked smartphone app suggests healthier alternatives when the red light comes on.
Following his son’s acute illness, Toumazou also invented a microchip that can read an individual’s DNA from a simple mouth swab sample. It’s now used to upload a DNA profile to the new wristband – a process that takes an hour instead of up to eight weeks for a conventional DNA test.
“We’re not telling people they can’t eat biscuits, that they should eat grapes. No, they can eat biscuits, but eat the better biscuits based upon your DNA and lifestyle,” says Toumazou.
“It’s using biology to nudge and guide you to have a healthier lifestyle in the long term.”
What is the World Economic Forum doing about the Fourth Industrial Revolution?
Show
Keep moving
The device also helps to promote overall health by warning if you are inactive for too long. An orange light means it’s time to get up and move about.
One in 10 people with pre-diabetes, a reversible condition, will go on to develop type 2 diabetes, which affects more than 400 million people worldwide. Early diagnosis can enable people to change their lifestyles and avoid developing the full-blown condition.
And what about Toumazou’s son Marcus? Well, his story has a happy ending. After months in dialysis he received a kidney transplant and is now in good health.
He even met the Queen at the opening of his father’s new lab in London. He told her his father was changing healthcare by making microchips for the human body.Share License and Republishing
World Economic Forum articles may be republished in accordance with our Terms of Use.Written by
Douglas Broom, Senior Writer, Formative Content
The views expressed in this article are those of the author alone and not the World Economic Forum.Subscribe for updatesA weekly update of what’s on the Global Agenda
Featured: Future of Health and HealthcareView all
This wristband tells you what food to buy based on your DNADouglas Broom 15 Nov 2019These 10 countries are the best prepared to fight a pandemicNiall McCarthy · Statista 15 Nov 2019This at-home test could change cervical cancer screeningJake Ellison · Futurity 15 Nov 2019Making the most of our ‘extra time’ – for ourselves and societyCamilla Cavendish 15 Nov 2019How to stay fit in your 60s and beyondJulie Broderick · The Conversation 14 Nov 2019Female doctors are good for your health, but they experience a gender pay gap, discrimination, burnout and depressionRebecca Renkas · The Conversation 06 Nov 2019If you want to live longer and healthier, this is why you should runŽeljko Pedišić · The Conversation 05 Nov 2019Subscribe for updatesA weekly update of what’s on the Global AgendaFollow Us AboutOur MissionLeadership and GovernanceCommunitiesOur Members and PartnersGlobalization 4.0The Fourth Industrial RevolutionCentre for the Fourth Industrial RevolutionOur ImpactHistoryCentre for CybersecurityKlaus SchwabMediaPicturesCareersOpen ForumContact UsStrategic IntelligenceWorld Economic Forum LLCCode of ConductWorld Economic Forum Privacy PolicySustainabilityMediaNewsAccreditationSubscribe to our newsMembers & PartnersMember login to TopLinkStrategic Partners’ areaPartner Institutes’ areaGlobal sitesCentre for the Fourth Industrial RevolutionCentre for CybersecurityOpen ForumGlobal ShapersSchwab Foundation for Social EntrepreneurshipStrategic IntelligenceENESFR中文日本語© 2019 World Economic ForumPrivacy Policy & Terms of Service

NEURO FRONTIERREASONING 15 VIEWS
Protecting Teens’ Mental Health Is A Wise Investment

The neurological pathways between the ‘lower’ emotional, pleasure-seeking and impulsive centers and the ‘higher’ cortical regions that consider alternative solutions, consequences of actions, and utilize logic and reasoning to offset emotional pressures are still in the process of formation, according to a report. Technically, the adult architecture of the brain — that is, the myelination of the neurons — is not yet fully established. So, youth still tend to be ruled by feeling, impulse, and pleasure-seeking — which really complicates decision making and behavior in highly charged situations.
The struggles teens face transitioning from the supportive, although many times highly competitive, the environment of high school to the mountainous expectations and life-altering outcomes at college can be overwhelming. These challenges often increase teen anxiety and inflame feelings of hopelessness and isolation. It is especially dangerous for students already suffering from clinical anxiety and depression. The rates of suicide ideation among college students are alarming.
The key to addressing this health care crisis is raising awareness among students, parents, professors, and staff to recognize symptoms of heightened stress and anxiety.
Source: KiplingerPREVIOUS ARTICLECircuit Responsible For Building Memories IdentifiedNEXT ARTICLEUnderstanding Self-Sabotage: The Enemy Within
Contribute & Collaborate
You can contribute your articles on emerging fields to Pioneering Minds. You can also collaborate with Pioneering Minds on patents within various categories of emerging fields like AI, Space Exploration, Nanomaterials, Autonomous Vehicles, DNA Editing, Robotics, IOT, Quantum Computing, Wearables, 3D Printing, Cryptocurrency, Energy Storage, Neurophotonics and other.
Pioneering Minds
Follow Us
Twitter Feed
© 2017-2019 Pioneering Minds

Reality
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopediaJump to navigationJump to searchFor other uses, see Reality (disambiguation).Not to be confused with Realty.
Reality is the sum or aggregate of all that is real or existent within a system, as opposed to that which is only imaginary. The term is also used to refer to the ontological status of things, indicating their existence.[1] In physical terms, reality is the totality of a system, known and unknown.[2] Philosophical questions about the nature of reality or existence or being are considered under the rubric of ontology, which is a major branch of metaphysics in the Western philosophical tradition. Ontological questions also feature in diverse branches of philosophy, including the philosophy of science, philosophy of religion, philosophy of mathematics, and philosophical logic. These include questions about whether only physical objects are real (i.e., Physicalism), whether reality is fundamentally immaterial (e.g., Idealism), whether hypothetical unobservable entities posited by scientific theories exist, whether God exists, whether numbers and other abstract objects exist, and whether possible worlds exist.
Contents
- 1Related concepts
- 2Western philosophy
- 3Jain philosophy
- 4Physical sciences
- 5Technology
- 6See also
- 7Notes
- 8References
- 9Further reading
- 10External links
Related concepts
World views and theories
Further information: World view
A common colloquial usage would have reality mean “perceptions, beliefs, and attitudes toward reality”, as in “My reality is not your reality.” This is often used just as a colloquialism indicating that the parties to a conversation agree, or should agree, not to quibble over deeply different conceptions of what is real. For example, in a religious discussion between friends, one might say (attempting humor), “You might disagree, but in my reality, everyone goes to heaven.”
Reality can be defined in a way that links it to worldviews or parts of them (conceptual frameworks): Reality is the totality of all things, structures (actual and conceptual), events (past and present) and phenomena, whether observable or not. It is what a world view (whether it be based on individual or shared human experience) ultimately attempts to describe or map.
Certain ideas from physics, philosophy, sociology, literary criticism, and other fields shape various theories of reality. One such belief is that there simply and literally is no reality beyond the perceptions or beliefs we each have about reality. Such attitudes are summarized in the popular statement, “Perception is reality” or “Life is how you perceive reality” or “reality is what you can get away with” (Robert Anton Wilson), and they indicate anti-realism – that is, the view that there is no objective reality, whether acknowledged explicitly or not.
Many of the concepts of science and philosophy are often defined culturally and socially. This idea was elaborated by Thomas Kuhn in his book The Structure of Scientific Revolutions (1962). The Social Construction of Reality, a book about the sociology of knowledge written by Peter L. Berger and Thomas Luckmann, was published in 1966. It explained how knowledge is acquired and used for the comprehension of reality. Out of all the realities, the reality of everyday life is the most important one since our consciousness requires us to be completely aware and attentive to the experience of everyday life.
Western philosophy
Philosophy addresses two different aspects of the topic of reality: the nature of reality itself, and the relationship between the mind (as well as language and culture) and reality.
On the one hand, ontology is the study of being, and the central topic of the field is couched, variously, in terms of being, existence, “what is”, and reality. The task in ontology is to describe the most general categories of reality and how they are interrelated. If a philosopher wanted to proffer a positive definition of the concept “reality”, it would be done under this heading. As explained above, some philosophers draw a distinction between reality and existence. In fact, many analytic philosophers today tend to avoid the term “real” and “reality” in discussing ontological issues. But for those who would treat “is real” the same way they treat “exists”, one of the leading questions of analytic philosophy has been whether existence (or reality) is a property of objects. It has been widely held by analytic philosophers that it is not a property at all, though this view has lost some ground in recent decades.
On the other hand, particularly in discussions of objectivity that have feet in both metaphysics and epistemology, philosophical discussions of “reality” often concern the ways in which reality is, or is not, in some way dependent upon (or, to use fashionable jargon, “constructed” out of) mental and cultural factors such as perceptions, beliefs, and other mental states, as well as cultural artifacts, such as religions and political movements, on up to the vague notion of a common cultural world view, or Weltanschauung.
The view that there is a reality independent of any beliefs, perceptions, etc., is called realism. More specifically, philosophers are given to speaking about “realism about” this and that, such as realism about universals or realism about the external world. Generally, where one can identify any class of object, the existence or essential characteristics of which is said not to depend on perceptions, beliefs, language, or any other human artifact, one can speak of “realism about” that object.
One can also speak of anti-realism about the same objects. Anti-realism is the latest in a long series of terms for views opposed to realism. Perhaps the first was idealism, so called because reality was said to be in the mind, or a product of our ideas. Berkeleyan idealism is the view, propounded by the Irish empiricist George Berkeley, that the objects of perception are actually ideas in the mind. In this view, one might be tempted to say that reality is a “mental construct”; this is not quite accurate, however, since, in Berkeley’s view, perceptual ideas are created and coordinated by God. By the 20th century, views similar to Berkeley’s were called phenomenalism. Phenomenalism differs from Berkeleyan idealism primarily in that Berkeley believed that minds, or souls, are not merely ideas nor made up of ideas, whereas varieties of phenomenalism, such as that advocated by Russell, tended to go farther to say that the mind itself is merely a collection of perceptions, memories, etc., and that there is no mind or soul over and above such mental events. Finally, anti-realism became a fashionable term for any view which held that the existence of some object depends upon the mind or cultural artifacts. The view that the so-called external world is really merely a social, or cultural, artifact, called social constructionism, is one variety of anti-realism. Cultural relativism is the view that social issues such as morality are not absolute, but at least partially cultural artifact.
A correspondence theory of knowledge about what exists claims that “true” knowledge of reality represents accurate correspondence of statements about and images of reality with the actual reality that the statements or images are attempting to represent. For example, the scientific method can verify that a statement is true based on the observable evidence that a thing exists. Many humans can point to the Rocky Mountains and say that this mountain range exists, and continues to exist even if no one is observing it or making statements about it.
Being
The nature of being is a perennial topic in metaphysics. For, instance Parmenides taught that reality was a single unchanging Being, whereas Heraclitus wrote that all things flow. The 20th century philosopher Heidegger thought previous philosophers have lost sight the question of Being (qua Being) in favour of the questions of beings (existing things), so that a return to the Parmenidean approach was needed. An ontological catalogue is an attempt to list the fundamental constituents of reality. The question of whether or not existence is a predicate has been discussed since the Early Modern period, not least in relation to the ontological argument for the existence of God. Existence, that something is, has been contrasted with essence, the question of what something is. Since existence without essence seems blank, it associated with nothingness by philosophers such as Hegel. Nihilism represents an extremely negative view of being, the absolute a positive one.
Perception
The question of direct or “naïve” realism, as opposed to indirect or “representational” realism, arises in the philosophy of perception and of mind out of the debate over the nature of conscious experience;[3][4] the epistemological question of whether the world we see around us is the real world itself or merely an internal perceptual copy of that world generated by neural processes in our brain. Naïve realism is known as direct realism when developed to counter indirect or representative realism, also known as epistemological dualism,[5] the philosophical position that our conscious experience is not of the real world itself but of an internal representation, a miniature virtual-reality replica of the world.
Timothy Leary coined the influential term Reality Tunnel, by which he means a kind of representative realism. The theory states that, with a subconscious set of mental filters formed from their beliefs and experiences, every individual interprets the same world differently, hence “Truth is in the eye of the beholder”. His ideas influenced the work of his friend Robert Anton Wilson.
Abstract objects and mathematics
The status of abstract entities, particularly numbers, is a topic of discussion in mathematics.
In the philosophy of mathematics, the best known form of realism about numbers is Platonic realism, which grants them abstract, immaterial existence. Other forms of realism identify mathematics with the concrete physical universe.
Anti-realist stances include formalism and fictionalism.
Some approaches are selectively realistic about some mathematical objects but not others. Finitism rejects infinite quantities. Ultra-finitism accepts finite quantities up to a certain amount. Constructivism and intuitionism are realistic about objects that can be explicitly constructed, but reject the use of the principle of the excluded middle to prove existence by reductio ad absurdum.
The traditional debate has focused on whether an abstract (immaterial, intelligible) realm of numbers has existed in addition to the physical (sensible, concrete) world. A recent development is the mathematical universe hypothesis, the theory that only a mathematical world exists, with the finite, physical world being an illusion within it.
An extreme form of realism about mathematics is the mathematical multiverse hypothesis advanced by Max Tegmark. Tegmark’s sole postulate is: All structures that exist mathematically also exist physically. That is, in the sense that “in those [worlds] complex enough to contain self-aware substructures [they] will subjectively perceive themselves as existing in a physically ‘real’ world”.[6][7] The hypothesis suggests that worlds corresponding to different sets of initial conditions, physical constants, or altogether different equations should be considered real. The theory can be considered a form of Platonism in that it posits the existence of mathematical entities, but can also be considered a mathematical monism in that it denies that anything exists except mathematical objects.
Properties
Main article: Problem of universals
The problem of universals is an ancient problem in metaphysics about whether universals exist. Universals are general or abstract qualities, characteristics, properties, kinds or relations, such as being male/female, solid/liquid/gas or a certain colour,[8] that can be predicated of individuals or particulars or that individuals or particulars can be regarded as sharing or participating in. For example, Scott, Pat, and Chris have in common the universal quality of being human or humanity.
The realist school claims that universals are real – they exist and are distinct from the particulars that instantiate them. There are various forms of realism. Two major forms are Platonic realism and Aristotelian realism.[9] Platonic realism is the view that universals are real entities and they exist independent of particulars. Aristotelian realism, on the other hand, is the view that universals are real entities, but their existence is dependent on the particulars that exemplify them.
Nominalism and conceptualism are the main forms of anti-realism about universals.
Time and space
Main article: Philosophy of space and time
A traditional realist position in ontology is that time and space have existence apart from the human mind. Idealists deny or doubt the existence of objects independent of the mind. Some anti-realists whose ontological position is that objects outside the mind do exist, nevertheless doubt the independent existence of time and space.
Kant, in the Critique of Pure Reason, described time as an a priori notion that, together with other a priori notions such as space, allows us to comprehend sense experience. Kant denies that either space or time are substance, entities in themselves, or learned by experience; he holds rather that both are elements of a systematic framework we use to structure our experience. Spatial measurements are used to quantify how far apart objects are, and temporal measurements are used to quantitatively compare the interval between (or duration of) events. Although space and time are held to be transcendentally ideal in this sense, they are also empirically real, i.e. not mere illusions.
Idealist writers such as J. M. E. McTaggart in The Unreality of Time have argued that time is an illusion.
As well as differing about the reality of time as a whole, metaphysical theories of time can differ in their ascriptions of reality to the past, present and future separately.
- Presentism holds that the past and future are unreal, and only an ever-changing present is real.
- The block universe theory, also known as Eternalism, holds that past, present and future are all real, but the passage of time is an illusion. It is often said to have a scientific basis in relativity.
- The growing block universe theory holds that past and present are real, but the future is not.
Time, and the related concepts of process and evolution are central to the system-building metaphysics of A. N. Whitehead and Charles Hartshorne.
Possible worlds
The term “possible world” goes back to Leibniz’s theory of possible worlds, used to analyse necessity, possibility, and similar modal notions. Modal realism is the view, notably propounded by David Kellogg Lewis, that all possible worlds are as real as the actual world. In short: the actual world is regarded as merely one among an infinite set of logically possible worlds, some “nearer” to the actual world and some more remote. Other theorists may use the Possible World framework to express and explore problems without committing to it ontologically. Possible world theory is related to alethic logic: a proposition is necessary if it is true in all possible worlds, and possible if it is true in at least one. The many worlds interpretation of quantum mechanics is a similar idea in science.
Theories of everything (TOE) and philosophy
Main article: Theory of everything (philosophy)
The philosophical implications of a physical TOE are frequently debated. For example, if philosophical physicalism is true, a physical TOE will coincide with a philosophical theory of everything.
The “system building” style of metaphysics attempts to answer all the important questions in a coherent way, providing a complete picture of the world. Plato and Aristotle could be said to be early examples of comprehensive systems. In the early modern period (17th and 18th centuries), the system-building scope of philosophy is often linked to the rationalist method of philosophy, that is the technique of deducing the nature of the world by pure a priori reason. Examples from the early modern period include the Leibniz‘s Monadology, Descartes‘s Dualism, Spinoza‘s Monism. Hegel‘s Absolute idealism and Whitehead‘s Process philosophy were later systems.
Other philosophers do not believe its techniques can aim so high. Some scientists think a more mathematical approach than philosophy is needed for a TOE, for instance Stephen Hawking wrote in A Brief History of Time that even if we had a TOE, it would necessarily be a set of equations. He wrote, “What is it that breathes fire into the equations and makes a universe for them to describe?”[10]
Phenomenological reality
On a much broader and more subjective level,[specify] private experiences, curiosity, inquiry, and the selectivity involved in personal interpretation of events shapes reality as seen by one and only one individual [11] and hence is called phenomenological. While this form of reality might be common to others as well, it could at times also be so unique to oneself as to never be experienced or agreed upon by anyone else. Much of the kind of experience deemed spiritual occurs on this level of reality.
Phenomenology is a philosophical method developed in the early years of the twentieth century by Edmund Husserl and a circle of followers at the universities of Göttingen and Munich in Germany. Subsequently, phenomenological themes were taken up by philosophers in France, the United States, and elsewhere, often in contexts far removed from Husserl’s work.
The word phenomenology comes from the Greek phainómenon, meaning “that which appears”, and lógos, meaning “study”. In Husserl’s conception, phenomenology is primarily concerned with making the structures of consciousness, and the phenomena which appear in acts of consciousness, objects of systematic reflection and analysis. Such reflection was to take place from a highly modified “first person” viewpoint, studying phenomena not as they appear to “my” consciousness, but to any consciousness whatsoever. Husserl believed that phenomenology could thus provide a firm basis for all human knowledge, including scientific knowledge, and could establish philosophy as a “rigorous science”.[12]
Husserl’s conception of phenomenology has been criticised and developed not only by himself, but also by his student and assistant Martin Heidegger, by existentialists, such as Maurice Merleau-Ponty, Jean-Paul Sartre, and by other philosophers, such as Paul Ricoeur, Emmanuel Levinas, and Dietrich von Hildebrand.[13]
Skeptical hypotheses
A brain in a vat that believes it is walking
Skeptical hypotheses in philosophy suggest that reality is very different from what we think it is; or at least that we cannot prove it is not. Examples include:
- The “Brain in a vat” hypothesis is cast in scientific terms. It supposes that one might be a disembodied brain kept alive in a vat, and fed false sensory signals, by a mad scientist. This is a premise of the film series, Matrix hypothesis.
- The “Dream argument” of Descartes and Zhuangzi supposes reality to be indistinguishable from a dream.
- Descartes’ Evil demon is a being “as clever and deceitful as he is powerful, who has directed his entire effort to misleading me.”
- The five minute hypothesis (or omphalos hypothesis or Last Thursdayism) suggests that the world was created recently together with records and traces indicating a greater age.
- The Matrix hypothesis or Simulated reality hypothesis suggest that we might be inside a computer simulation or virtual reality.
Jain philosophy
Main article: Tattva (Jainism)
Jain philosophy postulates that seven tattva (truths or fundamental principles) constitute reality.[14] These seven tattva are:[15]
- Jīva – The soul which is characterized by consciousness.
- Ajīva – The non-soul.
- Asrava – Influx of karma.
- Bandha – The bondage of karma.
- Samvara – Obstruction of the inflow of karmic matter into the soul.
- Nirjara – Shedding of karmas.
- Moksha – Liberation or Salvation, i.e. the complete annihilation of all karmic matter (bound with any particular soul).
Physical sciences
Scientific realism
Scientific realism is, at the most general level, the view that the world described by science (perhaps ideal science) is the real world, as it is, independent of what we might take it to be. Within philosophy of science, it is often framed as an answer to the question “how is the success of science to be explained?” The debate over what the success of science involves centers primarily on the status of entities that are not directly observable discussed by scientific theories. Generally, those who are scientific realists state that one can make reliable claims about these entities (viz., that they have the same ontological status) as directly observable entities, as opposed to instrumentalism. The most used and studied scientific theories today state more or less the truth.
Realism and locality in physics
Realism in the sense used by physicists does not equate to realism in metaphysics.[16] The latter is the claim that the world is mind-independent: that even if the results of a measurement do not pre-exist the act of measurement, that does not require that they are the creation of the observer. Furthermore, a mind-independent property does not have to be the value of some physical variable such as position or momentum. A property can be dispositional (or potential), i.e. it can be a tendency: in the way that glass objects tend to break, or are disposed to break, even if they do not actually break. Likewise, the mind-independent properties of quantum systems could consist of a tendency to respond to particular measurements with particular values with ascertainable probability.[17] Such an ontology would be metaphysically realistic, without being realistic in the physicist’s sense of “local realism” (which would require that a single value be produced with certainty).
A closely related term is counterfactual definiteness (CFD), used to refer to the claim that one can meaningfully speak of the definiteness of results of measurements that have not been performed (i.e. the ability to assume the existence of objects, and properties of objects, even when they have not been measured).
Local realism is a significant feature of classical mechanics, of general relativity, and of electrodynamics; but quantum mechanics has shown that quantum entanglement is possible. This was rejected by Einstein, who proposed the EPR paradox, but it was subsequently quantified by Bell’s inequalities.[18] If Bell’s inequalities are violated, either local realism or counterfactual definiteness must be incorrect; but some physicists dispute that experiments have demonstrated Bell’s violations, on the grounds that the sub-class of inhomogeneous Bell inequalities has not been tested or due to experimental limitations in the tests. Different interpretations of quantum mechanics violate different parts of local realism and/or counterfactual definiteness.
Role of the observer in quantum mechanics
See also: Quantum decoherence
The quantum mind–body problem refers to the philosophical discussions of the mind–body problem in the context of quantum mechanics. Since quantum mechanics involves quantum superpositions, which are not perceived by observers, some interpretations of quantum mechanics place conscious observers in a special position.
The founders of quantum mechanics debated the role of the observer, and of them, Wolfgang Pauli and Werner Heisenberg believed that it was the observer that produced collapse. This point of view, which was never fully endorsed by Niels Bohr, was denounced as mystical and anti-scientific by Albert Einstein. Pauli accepted the term, and described quantum mechanics as lucid mysticism.[19]
Heisenberg and Bohr always described quantum mechanics in logical positivist terms. Bohr also took an active interest in the philosophical implications of quantum theories such as his complementarity, for example.[20] He believed quantum theory offers a complete description of nature, albeit one that is simply ill-suited for everyday experiences – which are better described by classical mechanics and probability. Bohr never specified a demarcation line above which objects cease to be quantum and become classical. He believed that it was not a question of physics, but one of philosophy.
Eugene Wigner reformulated the “Schrödinger’s cat” thought experiment as “Wigner’s friend” and proposed that the consciousness of an observer is the demarcation line which precipitates collapse of the wave function, independent of any realist interpretation. Commonly known as “consciousness causes collapse“, this interpretation of quantum mechanics states that observation by a conscious observer is what makes the wave function collapse.
Multiverse
The multiverse is the hypothetical set of multiple possible universes (including the historical universe we consistently experience) that together comprise everything that exists: the entirety of space, time, matter, and energy as well as the physical laws and constants that describe them. The term was coined in 1895 by the American philosopher and psychologist William James.[21] In the many-worlds interpretation (MWI), one of the mainstream interpretations of quantum mechanics, there are an infinite number of universes and every possible quantum outcome occurs in at least one universe.
The structure of the multiverse, the nature of each universe within it and the relationship between the various constituent universes, depend on the specific multiverse hypothesis considered. Multiverses have been hypothesized in cosmology, physics, astronomy, religion, philosophy, transpersonal psychology and fiction, particularly in science fiction and fantasy. In these contexts, parallel universes are also called “alternative universes”, “quantum universes”, “interpenetrating dimensions”, “parallel dimensions”, “parallel worlds”, “alternative realities”, “alternative timelines”, and “dimensional planes”, among others.
Scientific theories of everything
A theory of everything (TOE) is a putative theory of theoretical physics that fully explains and links together all known physical phenomena, and predicts the outcome of any experiment that could be carried out in principle. The theory of everything is also called the final theory.[22] Many candidate theories of everything have been proposed by theoretical physicists during the twentieth century, but none have been confirmed experimentally. The primary problem in producing a TOE is that general relativity and quantum mechanics are hard to unify. This is one of the unsolved problems in physics.
Initially, the term “theory of everything” was used with an ironic connotation to refer to various overgeneralized theories. For example, a great-grandfather of Ijon Tichy, a character from a cycle of Stanisław Lem‘s science fiction stories of the 1960s, was known to work on the “General Theory of Everything”. Physicist John Ellis[23] claims to have introduced the term into the technical literature in an article in Nature in 1986.[24] Over time, the term stuck in popularizations of quantum physics to describe a theory that would unify or explain through a single model the theories of all fundamental interactions and of all particles of nature: general relativity for gravitation, and the standard model of elementary particle physics – which includes quantum mechanics – for electromagnetism, the two nuclear interactions, and the known elementary particles.
Current candidates for a theory of everything include string theory, M theory, and loop quantum gravity.
Technology
Virtual reality and cyberspace
Virtual reality (VR) is a computer-simulated environment that can simulate physical presence in places in the real world, as well as in imaginary worlds.Reality-Virtuality Continuum.
The Virtuality Continuum is a continuous scale ranging between the completely virtual, a Virtuality, and the completely real: Reality. The reality-virtuality continuum therefore encompasses all possible variations and compositions of real and virtual objects. It has been described as a concept in new media and computer science, but in fact it could be considered a matter of anthropology. The concept was first introduced by Paul Milgram.[25]
The area between the two extremes, where both the real and the virtual are mixed, is the so-called Mixed reality. This in turn is said to consist of both Augmented Reality, where the virtual augments the real, and Augmented virtuality, where the real augments the virtual. Cyberspace, the world’s computer systems considered as an interconnected whole, can be thought of as a virtual reality; for instance, it is portrayed as such in the cyberpunk fiction of William Gibson and others. Second life and MMORPGs such as World of Warcraft are examples of artificial environments or virtual worlds (falling some way short of full virtual reality) in cyberspace.
“RL” in internet culture
On the Internet, “real life” refers to life in the real world. It generally references life or consensus reality, in contrast to an environment seen as fiction or fantasy, such as virtual reality, lifelike experience, dreams, novels, or movies. Online, the acronym “IRL” stands for “in real life”, with the meaning “not on the Internet”.[26] Sociologists engaged in the study of the Internet have determined that someday, a distinction between online and real-life worlds may seem “quaint”, noting that certain types of online activity, such as sexual intrigues, have already made a full transition to complete legitimacy and “reality”.[27] The abbreviation “RL” stands for “real life”. For example, one can speak of “meeting in RL” someone whom one has met in a chat or on an Internet forum. It may also be used to express an inability to use the Internet for a time due to “RL problems”.
See also
Notes
- ^ “reality | Definition of reality in English by Oxford Dictionaries”. Oxford Dictionaries | English. Retrieved 2017-10-28.
- ^ Saridakis E. (2016). “Information, reality, and modern physics”. International Studies in the Philosophy of Science. 30: 327–341.
- ^ Lehar, Steve. (2000). The Function of Conscious Experience: An Analogical Paradigm of Perception and Behavior, Consciousness and Cognition.
- ^ Lehar, Steve. (2000). Naïve Realism in Contemporary Philosophy Archived 2012-08-11 at the Wayback Machine, The Function of Conscious Experience.
- ^ Lehar, Steve. Representationalism Archived 2012-09-05 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ Tegmark, Max (February 2008). “The Mathematical Universe”. Foundations of Physics. 38 (2): 101–150. arXiv:0704.0646. Bibcode:2008FoPh…38..101T. doi:10.1007/s10701-007-9186-9.
- ^ Tegmark (1998), p. 1.
- ^ Loux (2001), p. 4
- ^ Price (1953), among others, sometimes uses such Latin terms
- ^ as quoted in [Artigas, The Mind of the Universe, p.123]
- ^ Present-time consciousness Francisco J. Varela Journal of Consciousness Studies 6 (2-3):111-140 (1999)
- ^ Joseph Kockelmans (2001). Edmund Husserl’s phenomenology(2 ed.). Purdue University Press. pp. 311–314. ISBN 1-55753-050-5.
- ^ Steven Galt Crowell (2001). Husserl, Heidegger, and the space of meaning: paths toward transcendental phenomenology. Northwestern University Press. p. 160. ISBN 0-8101-1805-X.
- ^ S.A. Jain 1992, p. 6.
- ^ S.A. Jain 1992, p. 7.
- ^ Norsen, Travis (26 February 2007). “Against `Realism'”. Foundations of Physics. 37 (3): 311–340. arXiv:quant-ph/0607057. Bibcode:2007FoPh…37..311N. doi:10.1007/s10701-007-9104-1.
- ^ Thompson, Ian. “Generative Science”. http://www.generativescience.org.
- ^ “Local realism and the crucial experiment”. bendov.info.
- ^ Juan Miguel Marin (2009). “‘Mysticism’ in quantum mechanics: the forgotten controversy”. European Journal of Physics. 30 (4): 807–822. Bibcode:2009EJPh…30..807M. doi:10.1088/0143-0807/30/4/014. link, summarized here [1] Archived 2011-06-06 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ John Honner (2005). “Niels Bohr and the Mysticism of Nature”. Zygon: Journal of Religion & Science. 17–3: 243–253.
- ^ James, William, The Will to Believe, 1895; and earlier in 1895, as cited in OED‘s new 2003 entry for “multiverse”: “1895 W. JAMES in Internat. Jrnl. Ethics 6 10 Visible nature is all plasticity and indifference, a multiverse, as one might call it, and not a universe.”
- ^ Weinberg (1993)
- ^ Ellis, John (2002). “Physics gets physical (correspondence)”. Nature. 415 (6875): 957. Bibcode:2002Natur.415..957E. doi:10.1038/415957b. PMID 11875539.
- ^ Ellis, John (1986). “The Superstring: Theory of Everything, or of Nothing?”. Nature. 323 (6089): 595–598. Bibcode:1986Natur.323..595E. doi:10.1038/323595a0.
- ^ Milgram, Paul; H. Takemura; A. Utsumi; F. Kishino (1994). “Augmented Reality: A class of displays on the reality-virtuality continuum” (PDF). Proceedings of Telemanipulator and Telepresence Technologies. pp. 2351–34. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2006-10-04. Retrieved 2007-03-15.
- ^ “AcronymFinder.com search for IRL”.
- ^ Don Slater (2002). “Social Relationships and Identity On-line and Off-line”. In Leah, Sonia, Lievrouw, and Livingstone (eds.). Handbook of New Media: Social Shaping and Consequences of ICTs. Sage Publications Inc. pp. 533–543. ISBN 0-7619-6510-6.
References
- Berger, Peter L.; Luckmann, Thomas (1966). The Social Construction of Reality: A Treatise in the Sociology of Knowledge. New York: Anchor Books. pp. 21–22.
- Jain, S. A. (1992). Reality. Jwalamalini Trust. Archived from the original on 2015.
Not in Copyright
Further reading
- George Musser, “Virtual Reality: How close can physics bring us to a truly fundamental understanding of the world?”, Scientific American, vol. 321, no. 3 (September 2019), pp. 30–35. “Physics is… the bedrock of the broader search for truth…. Yet [physicists] sometimes seem to be struck by a collective imposter syndrome…. Truth can be elusive even in the best-established theories. Quantum mechanics is as well tested a theory as can be, yet its interpretation remains inscrutable. [p. 30.] The deeper physicists dive into reality, the more reality seems to evaporate.” [p. 34.]
External links
Realityat Wikipedia’s sister projects
 Definitions from Wiktionary
Definitions from Wiktionary Media from Wikimedia Commons
Media from Wikimedia Commons News from Wikinews
News from Wikinews Quotations from Wikiquote
Quotations from Wikiquote Texts from Wikisource
Texts from Wikisource Textbooks from Wikibooks
Textbooks from Wikibooks Resources from Wikiversity
Resources from Wikiversity
- Miller, Alexander. “David Lewis”. In Zalta, Edward N. (ed.). Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy.
- C.D. Broad on Reality
- Video: Animated version of the above with Dr Quantum – Flatland
- Phenomenology Online: Materials discussing and exemplifying phenomenological research
- The Matrix as Metaphysics by David Chalmers
- Reality
- Reality by type
- Aesthetics
- Abstraction
- Assumption
- Concepts
- Concepts in aesthetics
- Concepts in ancient Greek aesthetics
- Concepts in ancient Greek metaphysics
- Concepts in ancient Greek philosophy of mind
- Concepts in epistemology
- Concepts in logic
- Concepts in metaphilosophy
- Concepts in metaphysics
- Concepts in the philosophy of language
- Concepts in the philosophy of mind
- Concepts in the philosophy of science
- Consensus reality
- Emergence
- Epistemology
- History of education
- History of ideas
- History of logic
- History of philosophy
- History of science
- Logic
- Metaphilosophy
- Metaphysics
- Ontology
- Philosophical concepts
- Philosophical theories
- Philosophy of culture
- Philosophy of language
- Philosophy of mathematics
- Philosophy of mind
- Philosophy of religion
- Philosophy of science
- Thought
- Truth
Navigation menu
- Not logged in
- Talk
- Contributions
- Create account
- Log in
Search
Interaction
Tools
- What links here
- Related changes
- Upload file
- Special pages
- Permanent link
- Page information
- Wikidata item
- Cite this page
In other projects
Print/export
Languages
- This page was last edited on 28 December 2019, at 19:38 (UTC).
- Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License; additional terms may apply. By using this site, you agree to the Terms of Use and Privacy Policy. Wikipedia® is a registered trademark of the Wikimedia Foundation, Inc., a non-profit organization.



This is very interesting, You are a very skilled blogger.
I’ve joined your rss feed and look forward to seeking more of your wonderful
post. Also, I’ve shared your website in my social networks!
LikeLike
nice!
LikeLike
Like!! Really appreciate you sharing this blog post.Really thank you! Keep writing.
LikeLike
Hmm is anyone else experiencing problems with
the images on this blog loading? I’m trying to
find out if its a problem on my end or if it’s the blog.
Any feedback would be greatly appreciated.
LikeLike
I’m really enjoying the design and layout of your website. It’s a very easy on the eyes which makes it much more enjoyable for me to come here and visit more often. Did you hire out a developer to create your theme? Excellent work!
LikeLike
Hi, the Elon Musk’s AI project to replicate the human brain receives $1 billion from Microsoft @ Links about: ´´Simulated reality – Is Reality
a Simulation?´´ & ´´Are we living in a computer simulation? ´´I don’t know.
Probably.´´ @ Google / Facebook / Time / Tempo
/ Countries / País @ SCIENTISTS ‘HAVE ACHIEVED QUANTUM
SUPREMACY’, IN DISCOVERY THAT COULD CHANGE THE WORLD
– What is the best animal model for Alzheimer’s disease?
@ Other Facts & ´´Reality is the sum or
aggregate of all that is real or existent within a system, as opposed to that which is only imaginary.
The term is also used to refer to the ontological status
of things, indicating their existence.[1] In physical terms, reality is the totality of a system, known and unknown.[2]´´ @ Links article
it is well written and was a pleasure to red it.
I have found a way to reduce the bills, which I share with you: http://bit.ly/cut-power-bills-by-65
Why pay more? 🙂 Many Kisses!
LikeLike
Where To Purchase Alli [url=http://apcialisle.com/#]Cialis[/url] Cialis Bewertung п»їcialis Ou Acheter Du Cialis Generique
LikeLike
Useful info. Lucky me I found your site accidentally, and I’m stunned
why this twist of fate didn’t took place earlier!
I bookmarked it.
LikeLike
Kamagra France Livraison Rapide [url=http://apcialisle.com/#]Buy Cialis[/url] Kamagra To You buy cialis online Overnight Viagra
LikeLike
Cheapest private proxies – prices as little as $0.15 a proxy! Obtain currently to get 50 price reduction for the proxy bundle – DreamProxies.com
LikeLike
I’ve come across that today, more and more people are now being attracted to camcorders and the industry of picture taking. However, as a photographer, you will need to first invest so much time frame deciding which model of camera to buy plus moving out of store to store just so you could possibly buy the least expensive camera of the brand you have decided to select. But it doesn’t end right now there. You also have to take into consideration whether you can purchase a digital photographic camera extended warranty. Thanks a bunch for the good guidelines I gained from your site.
LikeLike
I am impressed with this website , real I am a fan.
LikeLike
I really lucky to find this web site on bing, just what I was looking for : D too saved to fav.
LikeLike
Great article. I’m experiencing some of these issues as well..
LikeLike
Levitra Medicament 20mg [url=http://cialibuy.com/#]how to buy cialis[/url] Cialis 20mg Cialis Combivir
LikeLike
What’s up, this weekend is pleasant in favor of
me, because this point in time i am reading this great educational article here at my residence.
LikeLike
Wow, incredible blog layout! How long have you been blogging for? you make blogging look easy. The overall look of your site is wonderful, as well as the content!
LikeLike
These are actually great ideas in concerning blogging.
LikeLike
These are actually great ideas in concerning blogging.
LikeLike
I love your wordpress web template, wherever would you download it from?
LikeLike
Levaquin Ups Internet Next Day [url=https://buycialisuss.com/#]real cialis online[/url] Metronidazole 500mg Tablets Amazon Buy Cialis Cytotec Et Cialis
LikeLike
Your style is unique compared to other people I have read stuff from. I appreciate you for posting when you have the opportunity, Guess I’ll just bookmark this blog.
LikeLike
Hi! Would you mind if I share your blog with my zynga group?
There’s a lot of people that I think would really enjoy your content.
Please let me know. Cheers
LikeLike
Wonderful blog! I found it while browsing on Yahoo News. Do you have any suggestions on how to get listed in Yahoo News? I’ve been trying for a while but I never seem to get there! Many thanks
LikeLike
Hello are using WordPress for your site platform? I’m new to the blog world but I’m trying to get started and set up my own. Do you require any html coding knowledge to make your own blog? Any help would be really appreciated!
LikeLike
Howdy! Do you know if they make any plugins to safeguard against hackers? I’m kinda paranoid about losing everything I’ve worked hard on. Any tips?
LikeLike
Greetings! This is my 1st comment here so I just wanted to give a quick shout out and say I really enjoy reading your posts. Can you recommend any other blogs/websites/forums that go over the same topics? Appreciate it!
LikeLike
These are actually great ideas in concerning blogging.
LikeLike
Jenes Thema interessiert mich sehr, könnten Sie evtl. konkreter erläutern, wie man zu weiteren Informationen zu dem Thema gelangen kann?
LikeLike
Hello Admin,
YOU NEED QUALITY VISITORS for your: wordpress.com
My name is Fatima Simone, and I’m a Web Traffic Specialist. I can get:
– visitors from search engines
– visitors from social media
– visitors from any country you want
– very low bounce rate & long visit duration
CLAIM YOUR 24 HOURS FREE TEST => https://bit.ly/3gqLEoE
Do not forget to read Review to convince you, is already being tested by many people who have trusted it !!
Elon Musk’s AI project to replicate the human brain receives $1 billion from Microsoft @ Links about: ´´Simulated reality – Is Reality a Simulation?´´ & ´´Are we living in a computer simulation? ´´I don’t know. Probably.´´ @ Google / Facebook / Time / Tempo / Countries / País @ SCIENTISTS ‘HAVE ACHIEVED QUANTUM SUPREMACY’, IN DISCOVERY THAT COULD CHANGE THE WORLD – What is the best animal model for Alzheimer’s disease? @ Other Facts & ´´Reality is the sum or aggregate of all that is real or existent within a system, as opposed to that which is only imaginary. The term is also used to refer to the ontological status of things, indicating their existence.[1] In physical terms, reality is the totality of a system, known and unknown.[2]´´ @ Links – Science, technology and innovation @ Rodrigo Nunes Cal
LikeLike
The best SEO & Most Powerful link building software for your business.
I just checked out your website wordpress.com and wanted to find out if you need help for SEO Link Building ?
If you aren’t using SEO Software then you will know the amount of work load involved in creating accounts, confirming emails and submitting your contents to thousands of websites.
With THIS SOFTWARE the link submission process will be the easiest task and completely automated, you will be able to build unlimited number of links and increase traffic to your websites which will lead to a higher number of customers and much more sales for you.
IF YOU ARE INTERESTED, We offer you 7 days free trial => https://bit.ly/3ebnYTI
LikeLike
Levitra Generico Torino Esotaabsor [url=https://ascialis.com/#]Cialis[/url] FLOONSNURO Baclofene Cancer Hemsemboto can i buy cialis without a prescription unfokeones Propecia From China
LikeLike
One other issue is that if you are in a situation where you do not possess a co-signer then you may really want to try to wear out all of your educational funding options. You can get many funds and other scholarships that will present you with funding to assist with college expenses. Thanks alot : ) for the post.
LikeLike
Really appreciate you sharing this article post.Many thanks. I want more 🙂
LikeLike
Has anyone shopped at E-Cig Warehouse Vape Store in 3678 Falls Rd?
LikeLike
Best view i have ever seen !
LikeLike
I used to be able to find good info from your content.
LikeLike
Right here is the perfect web site for anyone who wants to understand this topic. You understand a whole lot its almost hard to argue with you (not that I actually will need toÖHaHa). You definitely put a brand new spin on a subject which has been written about for years. Excellent stuff, just wonderful!
LikeLike
Hi, I do think this is an excellent blog. I stumbledupon it 😉 I am going to return once again since i have saved as a favorite it. Money and freedom is the best way to change, may you be rich and continue to guide other people.
LikeLike
bookmarked!!, I like your blog!
LikeLike
Hello! I could have sworn Iíve visited this website before but after looking at many of the posts I realized itís new to me. Regardless, Iím certainly delighted I came across it and Iíll be book-marking it and checking back regularly!
LikeLike
Best view i have ever seen !
LikeLike
Howdy! I could have sworn Iíve visited this site before but after going through some of the articles I realized itís new to me. Nonetheless, Iím certainly happy I discovered it and Iíll be bookmarking it and checking back often!
LikeLike
You’ve been a great help to me. Thank you!
LikeLike
I was very happy to uncover this web site. I want to to thank you for your time just for this fantastic read!! I definitely really liked every little bit of it and I have you book marked to see new stuff on your site.
LikeLike
Extraordinary is an all-in-one life management system that helps you get more performed in less time.
LikeLike
I have to thank you for the efforts you have put in writing this blog. I’m hoping to check out the same high-grade content from you in the future as well. In truth, your creative writing abilities has encouraged me to get my very own site now 😉
LikeLike
Currently, picture just how much more great life could be with this amazing item that aids make it all happen!
LikeLike
cbd bud delta 8
LikeLike
Phenomenal is the one-stop service to aid you get more done in life.
LikeLike
This can do the trick!
LikeLike
Enjoy the advantages of a healthy, lavish and satisfied life with this outstanding item.
LikeLike
You’ll have even more time to give and also do what issues with this.
LikeLike
How? Discover currently!
LikeLike
From performance to connections, this one adjustment will certainly make whatever much better.
LikeLike
The Phenomenal will certainly help you intend your days, weeks and also months with ease to ensure you’re obtaining one of the most out of life!
LikeLike
Sensational is an all-in-one time monitoring remedy that will aid you be much more effective than in the past!
LikeLike
Presenting the Amazingness life-altering productivity supplement!
LikeLike
The most fantastic service for getting points ended up. This is precisely what your life needs.
LikeLike
Outstanding advantages of this are unmatched!
LikeLike
This will certainly alter the way you do points from now on.
LikeLike
Remarkable is the ideal name for this item.
LikeLike
Sensational is the one stop look for everything productivity!
LikeLike
Presenting the Amazingness life hack. This straightforward change will make your days more effective and cheerful .
LikeLike
Already counting the minutes until we’re together cvvme gain!
LikeLike
Get the fire department on briansclub cm he phone…we have a hottie alert!
LikeLike
What i do not realize is in reality how you’re not actually much more well-favored than you may be now. You’re so intelligent. You recognize thus significantly in terms of this topic, made me in my opinion consider it from so many varied angles. Its like women and men are not involved except it is something to do with Girl gaga! Your personal stuffs outstanding. Always deal with it up!
LikeLike
You can have the best time of your life with this item if you use it!
LikeLike
You never fail to impress me? feshop
LikeLike
My role model ❤️ feshop
LikeLike
Are you signing feshop utographs?
LikeLike
The most impressive solution for getting points ended up. This is specifically what your life requires.
LikeLike
Register currently and also start on your journey today!
LikeLike
With more than 61,000 members, CoinDCX Pro Telegram group is one of the largest crypto community,feshop keeping people up-to-date with the crypto industry. It’s also a great place to network and interact with amazing people from across the country.
LikeLike
All aboard the Hot Mess fe acc18 ru xpress.
LikeLike
Absolutely nothing can be like this!
LikeLike
Amazingness will certainly transform your life right.
LikeLike
This is mood ❤️ fe acc18 ru
LikeLike
Now that’s a lovely pic 💖 fe acc18 ru
LikeLike
The beauty of blockchain and crypto communities is that they are usually spread across the world and there are many choices. fe-acc18.ru
LikeLike
I adore you 💖 Looking so fine, where did you do your makeover? cvvme
LikeLike
He/she is my best friend, everyone. cvvme
LikeLike
Prior to last week’s news, Bankman-Fried was a prominent face in Washington D.C, cvvme telling a banking conference last month that he spent much of his time.
LikeLike
You look gorgeous in this. I’m stunned!fe acc18 ru
LikeLike
I?ll immediately seize your rss as I can’t to find your e-mail subscription hyperlink or newsletter service. Do you have any? Please permit me understand so that I may just subscribe. Thanks.
LikeLike
It’s a pity you don’t have a donate button! I’d without a doubt donate to this brilliant blog! I suppose for now i’ll settle for book-marking and adding your RSS feed to my Google account. I look forward to fresh updates and will talk about this site with my Facebook group. Talk soon!|
LikeLike
Hi there every one, here every person is sharing these experience, thus it’s pleasant to read this blog, and I used to visit this web site all the time.|
LikeLike
whoah this blog is magnificent i love reading your posts. Keep up the good work! You know, lots of people are hunting around for this info, you could help them greatly.
LikeLike
You deserve the most effective life has to use. Amazingness is below to assist you get it!
LikeLike
Amazingness will alter your life for the better.
LikeLike
My developer is trying to convince me to move to .net from PHP. I have always disliked the idea because of the expenses. But he’s tryiong none the less. I’ve been using Movable-type on various websites for about a year and am anxious about switching to another platform. I have heard good things about blogengine.net. Is there a way I can import all my wordpress content into it? Any help would be really appreciated!|
LikeLike
2156
LikeLike
Dear wordpress.com administrator, Your posts are always well-referenced and credible.
LikeLike
Be better, much more innovative, and more effective!
LikeLike
The Phenomenal will assist you prepare your days, weeks and also months easily to ensure you’re getting the most out of life!
LikeLike
You will certainly never ever have to stress over obtaining anything done again.
LikeLike
Amazingness is a way of living that shoots one’s capacity to do wonders.
LikeLike
Check out just how this set tool can change your life right!
LikeLike
Be the very best at every little thing you do!
LikeLike
The Amazingness life management tool will certainly help you take your productivity to the following degree!
LikeLike
Amazing is the supreme social productivity application.
LikeLike
Incredible is a special productivity tool that can change your life.
LikeLike
I like the helpful information you provide in your articles. I?ll bookmark your blog and check again here frequently. I am quite sure I will learn a lot of new stuff right here! Good luck for the next!
LikeLike
It is my belief that mesothelioma is usually the most deadly cancer. It contains unusual attributes. The more I look at it the harder I am confident it does not act like a real solid cells cancer. In case mesothelioma is often a rogue viral infection, therefore there is the prospects for developing a vaccine as well as offering vaccination to asbestos exposed people who are open to high risk connected with developing long term asbestos associated malignancies. Thanks for sharing your ideas about this important ailment.
LikeLike
Hi my family member! I wish to say that this post is awesome, nice written and come with approximately all vital infos. I?d like to look extra posts like this .
LikeLike
https://download-install.com/entry/ED959CEAB880EBB7B0EC96B4-EBACB4EBA38C-EB8BA4EC9AB4EBA19CEB939C-ED959CECBBB4EC98A4ED94BCEC8AA4
LikeLike
Thanks for making me to get new strategies about computer systems. I also contain the belief that certain of the best ways to maintain your mobile computer in excellent condition has been a hard plastic material case, as well as shell, that fits over the top of one’s computer. A lot of these protective gear are model targeted since they are manufactured to fit perfectly within the natural covering. You can buy these directly from the seller, or through third party sources if they are available for your laptop computer, however not every laptop may have a cover on the market. Once more, thanks for your ideas.
LikeLike
“Exciting digital opportunities available in ppc derby Nottingham for those with experience in , PPC, and social media.”
LikeLike
The Amazingness is the excellent way to get more out of your life.
LikeLike
The Amazingness is the perfect way to obtain more out of your life.
LikeLike
states with delta 8 ban
LikeLike
full send gummies delta 8 review
LikeLike
One thing I have actually noticed is that often there are plenty of beliefs regarding the finance institutions intentions whenever talking about foreclosure. One fable in particular would be the fact the bank wants your house. Your banker wants your money, not your house. They want the cash they gave you together with interest. Avoiding the bank will undoubtedly draw some sort of foreclosed final result. Thanks for your write-up.
LikeLike
Great post! I found the blog to be both informative and well-presented. Bravo.
LikeLike
Discover the most effective habits of effective individuals.
LikeLike
It’s something brand-new. Simply amazing!
LikeLike
Thanks for your text. I would love to say that a health insurance specialist also works for the benefit of the particular coordinators of a group insurance policy. The health insurance agent is given a long list of benefits desired by anyone or a group coordinator. Exactly what a broker will is try to find individuals or perhaps coordinators that best complement those wants. Then he gifts his suggestions and if all sides agree, the broker formulates a binding agreement between the 2 parties.
LikeLike
Mind instructor that works in 10 mins a day.
LikeLike
I do agree with all the ideas you’ve presented in your post. They’re really convincing and will definitely work. Still, the posts are too short for newbies. Could you please extend them a little from next time? Thanks for the post.
LikeLike
There are some fascinating time limits on this article but I don?t know if I see all of them center to heart. There is some validity but I’ll take maintain opinion till I look into it further. Good article , thanks and we would like extra! Added to FeedBurner as nicely
LikeLike
I should say also believe that mesothelioma is a extraordinary form of melanoma that is typically found in those previously exposed to asbestos. Cancerous tissues form inside mesothelium, which is a defensive lining which covers many of the body’s body organs. These cells usually form while in the lining of the lungs, belly, or the sac which actually encircles the heart. Thanks for revealing your ideas.
LikeLike
Does your website have a contact page? I’m having trouble locating it but, I’d like to shoot you an e-mail. I’ve got some ideas for your blog you might be interested in hearing. Either way, great site and I look forward to seeing it improve over time.|
LikeLike
wonderful submit, very informative. I ponder why the opposite specialists of this sector don’t realize this. You should continue your writing. I am confident, you have a great readers’ base already!
LikeLike
This is the correct weblog for anyone who wants to seek out out about this topic. You realize a lot its nearly laborious to argue with you (not that I actually would want?HaHa). You definitely put a new spin on a topic thats been written about for years. Nice stuff, just great!
LikeLike
Introducing the one stop solution for a more productive life.
LikeLike
A container of Phenomenal that you can try for yourself!
LikeLike
It’s the ideal method to get every little thing done as well as lastly delight in a complete high quality life.
LikeLike
My brother recommended I might like this blog. He was totally right. This post truly made my day. You cann’t imagine simply how much time I had spent for this info! Thanks!
LikeLike
Hi there, I found your blog via Google at the same time as looking for a similar subject, your web site got here up, it seems great. I have bookmarked it in my google bookmarks.
LikeLike
I have not checked in here for a while since I thought it was getting boring, but the last several posts are good quality so I guess I?ll add you back to my everyday bloglist. You deserve it my friend 🙂
LikeLike
Thanks for the guidelines shared on the blog. Something also important I would like to state is that weight-loss is not supposed to be about going on a dietary fads and trying to lose as much weight as possible in a few months. The most effective way to lose weight naturally is by taking it slowly but surely and obeying some basic guidelines which can make it easier to make the most out of your attempt to slim down. You may know and already be following most of these tips, however reinforcing understanding never damages.
LikeLike
Wow that was odd. I just wrote an incredibly long comment but after I clicked submit my comment didn’t appear. Grrrr… well I’m not writing all that over again. Anyways, just wanted to say wonderful blog!
LikeLike
It’s the very best way to do everything!
LikeLike
In my opinion that a home foreclosure can have a important effect on the applicant’s life. Real estate foreclosures can have a Several to decade negative influence on a borrower’s credit report. A new borrower who may have applied for home financing or virtually any loans for instance, knows that the actual worse credit rating is definitely, the more hard it is to get a decent loan. In addition, it can affect any borrower’s ability to find a good place to let or rent, if that will become the alternative housing solution. Good blog post.
LikeLike
From efficiency to connections, this one adjustment will make every little thing far better.
LikeLike
how many drops of delta 8 tincture
LikeLike
The tools to assist you achieve your objectives and also make the most of the moment!
LikeLike
Incredible is a life altering tool that will certainly help you be a lot more efficient as well as get better outcomes.
LikeLike
This amazingness is a life changer!
LikeLike
Hello there!Are you looking for a way to make your t-shirt designs stand out? Look no further! We have the perfect solution foryou – our 18k t-shirts design bundles and 3500 t-shirt mockups from Bella.Click Here >>>https://bit.ly/3yDtudSImagine having access to a huge collection of unique and eye-catching designs that will make your t-shirts the envy of all your friends and customers. With our design bundles, you can easily find the perfect design for any occasion,whether it’s for a birthday, a special event, or just for fun.Click Here >>> https://bit.ly/3yDtudSAnd with our 3500 t-shirt mockups, you can see exactly how your designs will look in real life. No more guessing or wondering if your design will work – now you can see it for yourself!Click Here >>> https://bit.ly/3yDtudSBut that’s not all. Our designs are made from high-quality materials and are designed to last. You can trust that your t-shirts will look amazing and stay looking amazing for years to come.Click Here >>> https://bit.ly/3yDtudSSo what are you waiting for? Don’t miss out on this amazing opportunity to take your t-shirt designs to the next level. Order our 18k t-shirts design bundles and 3500 t-shirt mockups from Bella today and get ready to wow everyone with your incredible designs!
LikeLike
Achieving goals, success and also performance is a wind with Sensational!
LikeLike
Hey There. I found your blog using msn. This is a really well written article. I?ll be sure to bookmark it and return to read more of your useful information. Thanks for the post. I will definitely comeback.
LikeLike
Extraordinary is a efficiency booster that aids you get more done in much less time.
LikeLike
我印象深刻,我不得不说.真的 几乎没有我遇到过一个博客是both 教育和娱乐,让我让你知道,你有一语中的.你的idea是excellent;困难是某事,但不是足够 人是 说聪明.我非常快乐我在我的搜索某事中偶然发现了这个across 指的是这个.
LikeLike
Amazingness can help you transform your life right in means you never ever believed possible.
LikeLike
This is really interesting, You are a very skilled blogger. I’ve joined your feed and look forward to seeking more of your wonderful post. Also, I have shared your website in my social networks!
LikeLike
Hey! I just wish to give a huge thumbs up for the great info you have right here on this post. I might be coming again to your weblog for more soon.
LikeLike
Thanks a lot for sharing this with all of us you actually know what you are speaking approximately! Bookmarked. Kindly additionally visit my web site =). We will have a hyperlink alternate arrangement between us!
LikeLike
We’re a gaggle of volunteers and starting a new scheme in our community. Your site offered us with valuable information to work on. You’ve done a formidable process and our whole group will likely be thankful to you.
LikeLike
Best view i have ever seen !
LikeLike
You should have the very best of whatever in life. And this product can help you get there!
LikeLike
This simply might be the life-changing item you’ve been waiting for.
LikeLike
The Phenomenal will certainly assist you plan your days, weeks as well as months easily to see to it you’re obtaining one of the most out of life!
LikeLike
If you use it appropriate, you can have the best time of your life with this product!
LikeLike
Wow, marvelous blog layout! How long have you been blogging for? you made blogging look easy. The overall look of your web site is wonderful, let alone the content!
LikeLike
I know of the fact that now, more and more people will be attracted to cams and the issue of picture taking. However, being photographer, you must first shell out so much time frame deciding which model of digital camera to buy along with moving store to store just so you may buy the lowest priced camera of the brand you have decided to pick. But it would not end generally there. You also have to consider whether you should purchase a digital photographic camera extended warranty. Thx for the good points I acquired from your site.
LikeLike
Sensational is the only productivity device you require.
LikeLike
Extraordinary is a life altering tool that will help you be more productive as well as improve outcomes.
LikeLike
了不起 作品!这是 类型 信息 应该共享周围 网络. Disgrace the seek engines no longer 定位此 publish higher!过来和访问我的网站.谢谢 =)
LikeLike
I am not sure where you’re getting your information, but good topic. I needs to spend some time learning more or understanding more. Thanks for magnificent information I was looking for this information for my mission.
LikeLike
It’s straightforward when you have Amazingness in your life.
LikeLike
Incredible is one of the most reliable as well as reliable way to streamline your life.
LikeLike
Introducing the Amazingness life-changing performance supplement!
LikeLike
The Amazingness is here to assist you manage your time and also obtain even more out of life.
LikeLike
Just how? Amazingness can help you live an amazing life by offering you with the devices to be much more effective and also obtain more carried out in less time.
LikeLike
After I initially commented I clicked the -Notify me when new comments are added- checkbox and now every time a remark is added I get 4 emails with the identical comment. Is there any way you possibly can remove me from that service? Thanks!
LikeLike
There are definitely a variety of particulars like that to take into consideration. That may be a nice point to carry up. I offer the ideas above as general inspiration however clearly there are questions like the one you bring up where the most important thing will likely be working in trustworthy good faith. I don?t know if best practices have emerged around things like that, however I am positive that your job is clearly recognized as a good game. Both girls and boys really feel the impression of just a second?s pleasure, for the rest of their lives.
LikeLike
I have not checked in here for a while because I thought it was getting boring, but the last few posts are good quality so I guess I?ll add you back to my daily bloglist. You deserve it my friend 🙂
LikeLike
Extraordinary is an all-in-one time management toolkit that can aid you get even more performed in less time.
LikeLike
This amazingness is a life changer!
LikeLike
Phenomenal is a better method to work together as well as interact .
LikeLike
Amazingness can provide that for you!
LikeLike