Do the downloads!! Share!! The diffusion of very important information and knowledge is essential for the world progress always!! Thanks!!
- – > Mestrado – Dissertation – Tabelas, Figuras e Gráficos – Tables, Figures and Graphics – ´´My´´ Dissertation @ #Innovation #energy #life #health #Countries #Time #Researches #Reference #Graphics #Ages #Age #Mice #People #Person #Mouse #Genetics #PersonalizedMedicine #Diagnosis #Prognosis #Treatment #Disease #UnknownDiseases #Future #VeryEfficientDrugs #VeryEfficientVaccines #VeryEfficientTherapeuticalSubstances #Tests #Laboratories #Investments #Details #HumanLongevity #DNA #Cell #Memory #Physiology #Nanomedicine #Nanotechnology #Biochemistry #NewMedicalDevices #GeneticEngineering #Internet #History #Science #World
Pathol Res Pract. 2012 Jul 15;208(7):377-81. doi: 10.1016/j.prp.2012.04.006. Epub 2012 Jun 8.
The influence of physical activity in the progression of experimental lung cancer in mice
Renato Batista Paceli 1, Rodrigo Nunes Cal, Carlos Henrique Ferreira dos Santos, José Antonio Cordeiro, Cassiano Merussi Neiva, Kazuo Kawano Nagamine, Patrícia Maluf Cury
- PMID: 22683274
- DOI: 10.1016/j.prp.2012.04.006
Impact_Fator-wise_Top100Science_Journals
GRUPO_AF1 – GROUP AFA1 – Aerobic Physical Activity – Atividade Física Aeróbia – ´´My´´ Dissertation – Faculty of Medicine of Sao Jose do Rio Preto
GRUPO AFAN 1 – GROUP AFAN1 – Anaerobic Physical Activity – Atividade Física Anaeróbia – ´´My´´ Dissertation – Faculty of Medicine of Sao Jose do Rio Preto
GRUPO_AF2 – GROUP AFA2 – Aerobic Physical Activity – Atividade Física Aeróbia – ´´My´´ Dissertation – Faculty of Medicine of Sao Jose do Rio Preto
GRUPO AFAN 2 – GROUP AFAN 2 – Anaerobic Physical Activity – Atividade Física Anaeróbia – ´´My´´ Dissertation – Faculty of Medicine of Sao Jose do Rio Preto
Slides – mestrado – ´´My´´ Dissertation – Faculty of Medicine of Sao Jose do Rio Preto
CARCINÓGENO DMBA EM MODELOS EXPERIMENTAIS
DMBA CARCINOGEN IN EXPERIMENTAL MODELS
Avaliação da influência da atividade física aeróbia e anaeróbia na progressão do câncer de pulmão experimental – Summary – Resumo – ´´My´´ Dissertation – Faculty of Medicine of Sao Jose do Rio Preto
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/22683274/
Abstract
Lung cancer is one of the most incident neoplasms in the world, representing the main cause of mortality for cancer. Many epidemiologic studies have suggested that physical activity may reduce the risk of lung cancer, other works evaluate the effectiveness of the use of the physical activity in the suppression, remission and reduction of the recurrence of tumors. The aim of this study was to evaluate the effects of aerobic and anaerobic physical activity in the development and the progression of lung cancer. Lung tumors were induced with a dose of 3mg of urethane/kg, in 67 male Balb – C type mice, divided in three groups: group 1_24 mice treated with urethane and without physical activity; group 2_25 mice with urethane and subjected to aerobic swimming free exercise; group 3_18 mice with urethane, subjected to anaerobic swimming exercise with gradual loading 5-20% of body weight. All the animals were sacrificed after 20 weeks, and lung lesions were analyzed. The median number of lesions (nodules and hyperplasia) was 3.0 for group 1, 2.0 for group 2 and 1.5-3 (p=0.052). When comparing only the presence or absence of lesion, there was a decrease in the number of lesions in group 3 as compared with group 1 (p=0.03) but not in relation to group 2. There were no metastases or other changes in other organs. The anaerobic physical activity, but not aerobic, diminishes the incidence of experimental lung tumors.
Copyright © 2012 Elsevier GmbH. All rights reserved.
https://www.linkedin.com/pulse/top-6-most-amazing-ways-3d-printing-now-used-practice-bernard-marr
http://www.linkedin.com http://geneticeducation.co.in/role-of-dmso-in-pcr-dmso-a-pcr-enhancer/?fbclid=IwAR3-Lj5iY_3dvC7_PHkQ5iwB9HnzJmZiAx7kwF2XNInXqkYrK5KnrXYQmyA
http://www.google.com https://techgrabyte.com/googles-quantum-computer-10k-year-calculation-200-sec/?fbclid=IwAR2DHU-YKjwbNBJh9L4vhQClwuXE8kMWJZjSdTqeK0zzSngrA4A2cwVA9uI
https://www.facebook.com/quantum.astronaut/
https://www.facebook.com/pg/quantum.astronaut/about/?ref=page_internal
http://www.facebook.com/scientificblog
https://www.facebook.com/pg/CruzRoja.es/about/?ref=page_internal
https://www.facebook.com/CruzRoja.es/
https://www.quantamagazine.org/quantas-year-in-math-and-computer-science-2019-20191223/







The Year in Math and Computer Science
READ LATER
SHARE
COPIED!
NEXT: 2019 IN REVIEWThe Year in Biology
SERIES
2019 IN REVIEW
The Year in Math and Computer Science
Mathematicians and computer scientists made big progress in number theory, graph theory, machine learning and quantum computing, even as they reexamined our fundamental understanding of mathematics and neural networks.1
READ LATER
Olena Shmahalo/Quanta MagazineBill AndrewsSenior Editor
December 23, 2019
VIEW PDF/PRINT MODE2019 In ReviewComputer ScienceMachine LearningMathematicsNumber TheoryQuantum Computing
For mathematicians and computer scientists, this was often a year of double takes and closer looks. Some reexamined foundational principles, while others found shockingly simple proofs, new techniques or unexpected insights in long-standing problems. Some of these advances have broad applications in physics and other scientific disciplines. Others are purely for the sake of gaining new knowledge (or just having fun), with little to no known practical use at this time.
Quanta covered the decade-long effort to rid mathematics of the rigid equal sign and replace it with the more flexible concept of “equivalence.” We also wrote about emerging ideas for a general theory of neural networks, which could give computer scientists a coveted theoretical basis to understand why deep learning algorithms have been so wildly successful.
Meanwhile, ordinary mathematical objects like matrices and networks yielded unexpected new insights in short, elegant proofs, and decades-old problems in number theory suddenly gave way to new solutions. Mathematicians also learned more about how regularity and order arise from chaotic systems, random numbers and other seemingly messy arenas. And, like a steady drumbeat, machine learning continued to grow more powerful, altering the approach and scope of scientific research, while quantum computers (probably) hit a critical milestone.
Share this article
COPIED!
Newsletter
Get Quanta Magazine delivered to your inboxSubscribe nowMost recent newsletter
Ana Porta for Quanta Magazine
Building a Bedrock of Understanding
What if the equal sign — the bedrock of mathematics — was a mistake? A growing number of mathematicians, led in part by Jacob Lurie at the Institute for Advanced Study, want to rewrite their field, replacing “equality” with the looser language of “equivalence.” Currently, the foundations of mathematics are built with collections of objects called sets, but decades ago a pair of mathematicians began working with more versatile groupings called categories, which convey more information than sets and more possible relationships than equality. Since 2006, Lurie has produced thousands of dense pages of mathematical machinery describing how to translate modern math into the language of category theory.
More recently, other mathematicians have begun establishing the foundational principles of a field with no prevailing dogma to cast aside: neural networks. The technology behind today’s most successful machine learning algorithms is becoming increasingly indispensable in science and society, but no one truly understands how it works. In January, we reported on the ongoing efforts to build a theory of neural networks that explains how structure could affect a network’s abilities.
A New Look at Old Problems
Just because a path is familiar doesn’t mean it can’t still hold new secrets. Mathematicians, physicists and engineers have worked with mathematical terms called “eigenvalues” and “eigenvectors” for centuries, using them to describe matrices that detail how objects stretch, rotate or otherwise transform. In August, three physicists and a mathematician described a simple new formula they’d stumbled upon that relates the two eigen-terms in a new way – one that made the physicists’ work studying neutrinos much simpler while yielding new mathematical insights. After the article’s publication, the researchers learned that the relationship had been discovered and neglected multiple times before.
The familiar also gave way to novel insights in computer science, when a mathematician abruptly solved one of the biggest open problems in the field by proving the “sensitivity” conjecture, which describes how likely you are to affect the output of a circuit by changing a single input. The proof is disarmingly simple, compact enough to be summarized in a single tweet. And in the world of graph theory, another spartan paper (this one weighing in at just three pages) disproved a decades-old conjecture about how best to choose colors for the nodes of a network, a finding that affects maps, seating arrangements and sudokus.DVDP for Quanta Magazine
The Signal in the Noise
Mathematics often involves an imposition of order on disorder, a wresting of hidden structures out of the seemingly random. In May, a team used so-called magic functions to show that the best ways of arranging points in eight- and 24-dimensional spaces are also universally optimal – meaning they solve an infinite number of problems beyond sphere packing. It’s still not clear exactly why these magic functions should be so versatile. “There are some things in mathematics that you do by persistence and brute force,” said the mathematician Henry Cohn. “And then there are times like this where it’s like mathematics wants something to happen.”
Others also found patterns in the unpredictable. Sarah Peluse proved that numerical sequences called “polynomial progressions” are inevitable in large enough collections of numbers, even if the numbers are chosen randomly. Other mathematicians showed that under the right conditions, consistent patterns emerge from the doubly random process of analyzing in a random way the shapes produced by random means. Further cementing the link between disorder and meaning, Tim Austin proved in March that all mathematical descriptions of change are, ultimately, a mix of orderly and random systems – and even the orderly ones need a trace of randomness in them. Finally, in the real world, physicists have been working toward understanding when and how chaotic systems, from blinking fireflies to firing neurons, can synchronize and beat as one.
Playing With Numbers
We all learned how to multiply in elementary school, but in March, two mathematicians described an even better, faster method. Rather than multiply every digit with every other digit, which quickly grows untenable with big enough numbers, would-be multipliers can combine a series of techniques that includes adding, multiplying and rearranging digits to arrive at a product after significantly fewer steps. This may, in fact, be the most efficient possible way to multiply large numbers.
Other fun insights into the world of numbers this year include finally discovering a way to express 33 as the sum of three cubes, proving a long-standing conjecture about when you can approximate irrational numbers like pi and deepening the connections between the sums and products of a set of numbers.
Machine Learning’s Growing Pains
Scientists are increasingly turning to machines for help not just in acquiring data, but also in making sense of it. In March, we reported on the ways machine learning is changing how science is done. A process called generative modeling, for example, may be a “third way” to formulate and test hypotheses, after the more traditional means of observations and simulations – though many still see it as merely an improved method of processing information. Either way, Dan Falk wrote, it’s “changing the flavor of scientific discovery, and it’s certainly accelerating it.”
As for what the machines are helping us learn, researchers announced pattern-finding algorithms that have the potential to predict earthquakes in the Pacific Northwest, and a multidisciplinary team is decoding how vision works by creating a mathematical model based on brain anatomy. But there’s still far to go: A team in Germany announced that machines often fail at recognizing pictures because they focus on textures rather than on shapes, and a neural network nicknamed BERT learned to beat humans at reading comprehension tests, only for researchers to question whether the machine was truly comprehending or just getting better at test-taking.
Next Steps for Quantum Computers
After years of suspense, researchers finally achieved a major quantum computing milestone this year – though as with all things quantum, it’s a development suffused with uncertainty. Regular, classical computers are built from binary bits, but quantum computers instead use qubits, which exploit quantum rules to enhance computational power. In 2012, John Preskill coined the term “quantum supremacy” to describe the point at which a quantum computer outperforms a classical one. Reports of increasingly fast quantum systems led many insiders to suspect we would reach that point this year, and in October Google announced that the moment had finally arrived. A rival tech company, IBM, disagreed, however, arguing that Google’s claim deserved “a large dose of skepticism.” Nevertheless, the clear progress in building viable quantum computers over the years has also motivated researchers like Stephanie Wehner to build a next-generation, quantum internet.
The Quanta Newsletter
Get highlights of the most important news delivered to your email inboxSubscribe
Most recent newsletter
Also in Computer Science
Q&A
The Architect of Modern Algorithms
BySUSAN D’AGOSTINO
NOVEMBER 20, 201933
READ LATER
ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE
Playing Hide-and-Seek, Machines Invent New Tools
BySTEPHEN ORNES
NOVEMBER 18, 201910
READ LATER
ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE
Computers Evolve a New Path Toward Human Intelligence
ByMATTHEW HUTSON
NOVEMBER 6, 201950
READ LATER
Comment on this article
Quanta Magazine moderates comments to facilitate an informed, substantive, civil conversation. Abusive, profane, self-promotional, misleading, incoherent or off-topic comments will be rejected. Moderators are staffed during regular business hours (New York time) and can only accept comments written in English. Show comments
NEXT ARTICLE
Toward a Grand Unified Theory of Snowflakes
All Rights Reserved © 2019
RodrigoHomeFind FriendsCreateFriend RequestsMessagesNotificationsAccount Settings
Cruz Roja Española
@CruzRoja.esHomeFundraisersAboutEventsPhotosVideosReviewsPostsTelevision Cruz RojaDonar sangrePlayasNotesCommunityCreate a PageLikedFollowingShareMoreSend MessageAboutSuggest EditsBUSINESS INFO
Founded on July 6, 1864
MissionSus principales actividades se vinculan a servicios y programas de protección social y sanitaria: prestación de servicios socio sanitarios, atención a personas mayores, a refugiados e inmigrantes, a personas con discapacidad, a niños y jóvenes en riesgo o conflicto social, a personas reclusas, a mujeres en situación de riesgo… Pero también interviene en otros campos como la promoción y defensa de los Derechos Humanos y el Derecho Internacional Humanitario, o el desarrollo de acciones de voluntariado ambiental.CONTACT INFO
Call +34 900 221 122
@CruzRojaEspMORE INFO
AboutPágina Oficial de Cruz Roja Española. Cada vez más cerca de las personas.
Company OverviewCruz Roja es una de las principales organizaciones de voluntariado en España, una organización independiente y moderna.
Cruz Roja Española fue fundada en el añ… See More
General InformationHorario de atención: De lunes a viernes de 10 a 20 hrs (horario peninsular). Excepto festivos
Founding Date6 de julio de 1864
Privacy PolicycategoriesNonprofit Organization
Milestones2012
- 148º aniversario de la fundación de Cruz Roja Española
- 148º aniversario de la fundación de Cruz Roja Española
- 148º aniversario de la fundación de Cruz Roja Española
- 148º aniversario de la fundación de Cruz Roja Española
- 148º aniversario de la fundación de Cruz Roja Española
- About
- Create Ad
- Create Page
- Developers
- Careers
- Privacy
- Cookies
- Ad Choices
- Terms
- Help
- Settings
- Activity Log
Facebook © 2019
- English (US)
- Português (Brasil)
- Español
- Français (France)
- Italiano
- Deutsch
- العربية
- हिन्दी
- 中文(简体)
- 日本語
RodrigoHomeFind FriendsCreateFriend RequestsMessagesNotificationsAccount Settings
Quantum Astronaut
@quantum.astronautHomeAboutVideosPhotosPostsGroupsCommunityCreate a PageLikedFollowingShareMoreWatch VideoSend MessageAboutSuggest EditsPAGE INFO
Founded in 2009
MissionThis page chronicles advances in quantum technology, astronaut training, next-generation spaceflight and NASA-trained commercial astronaut Christopher Altman.INTERESTS
Personal InterestsQuantum physics, quantum technology, quantum entanglement, spaceflight, future technologies, astronaut trainingCONTACT INFO
christopher.t.altman@gmail.com
http://www.superconducting.blogspot.com
entanglement_amplificationMORE INFO
AffiliationNASA, ESA, CSA, JAXA
AboutQuantum technologist, ARC Future Fellow PhD Scholar in Quantum Technology, NASA-trained commercial astronaut Christopher Altman | Director–CEO–Founder–Chief Scientist | Starlab
ImpressumChristopher Altman (Director of the Board, Chief Science Officer for the world’s first commercial astronaut corps)
Jonathan Dowling (pioneer and senior advisor … See More
To conduct new experiments. To create new technologies. To develop revolutionary, innovative applications to help solve humanity’s grand challenges. To inspire our next generation of scientists, researchers and engineers.
Founding DateChristopher Altman
BiographyChristopher Altman is a scientist, diplomat and aspiring astronaut working to apply tomorrow’s technologies to today’s global challenges. His research focus is … See More
AwardsARC Future Fellow,
Quantum Mechanics in Higher Dimensional Hilbert Spaces, International Academy Traunkirchen, Austria, with Anton Zeilinger
Austrian fellowship… See More
Personal Informationhttp://www.electricchain.org/quantum
http://superconducting.blogspot.com
https://everipedia.org/wiki/christopheraltman/… See MorecategoriesScientistSTORYThe Future of SpaceflightChristopher Altman is an American physicist, quantum technologist, international diplomat and NASA-trained commercial astronaut who began his scientific career with a world record-holding artificial intelligence project and a NASA/USAF–supported time travel division at multidisciplinary, “Deep Future” research institute Starlab, where his work…See MoreTEAM MEMBERS
- About
- Create Ad
- Create Page
- Developers
- Careers
- Privacy
- Cookies
- Ad Choices
- Terms
- Help
- Settings
- Activity Log
Facebook © 2019
- English (US)
- Português (Brasil)
- Español
- Français (France)
- Italiano
- Deutsch
- العربية
- हिन्दी
- 中文(简体)
- 日本語
Join our newsletter today for freeSubscribe Now


Techgrabyte
Machine Learning Deep Learning Artificial Intelligence
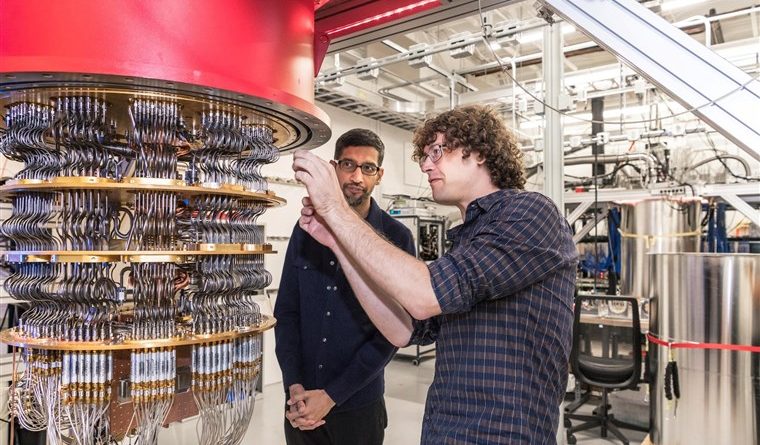

Google’s Quantum Computer Claims To Do 10k-year Calculation In Just 200 Seconds
- 6.14kShares
This week Google has achieved a massive milestone in the field of Quantum Computing that could completely revolutionize the methods of computing and the way we process data, the search engine giant is clamming unbelievable quantum computing results, the company said that they have achieved quantum supremacy.
Google has published there latest study in Nature, where they are clamming that their quantum system had executed a calculation in 200 seconds that would have taken a classic computer 10k years to complete.
In this new research paper, the scientists explain how they have designed, tested and developed a supreme quantum processor that could perform highly complex computational tasks in a time of 3 minutes.
In their official statement, Google said: “Our machine performed the target computation in 200 seconds, and from measurements, in our experiment, we determined that it would take the world’s fastest supercomputer 10,000 years to produce the similar output”.
The name of this quantum processor is Sycamore and it is of 54-qubit interconnected in a lattice pattern.
This quantum computer processor chip looks very much like a normal computer and it is placed in a casing at the bottom of structure shaped like an upside-down wedding cake, held in a vacuum chamber.
The environment is progressively colder with each tier until it’s at the 15-milliKelvin operating temperature. A mess of wires sends tiny microwave pulses to the qubit, causing it to take on excited states that are measured by another tiny component attached to the plus sign.
If we talk about our classical computer, they function in a binary fashion: they carry out tasks using tiny fragments of data known as bits that are only ever either 1 or 0. But fragments of data on a quantum computer, known as qubits, can be both 1 and 0 at the same time.
Each qubit is made from a tiny, plus sign-shaped loop of superconducting wire. This property, known as superposition, means a quantum computer, made up of several qubits, can crunch an enormous number of potential outcomes simultaneously, which ultimately leads to faster execution.
Google’s CEO Sundar Pichai said: “For those of us working in technology, it’s the ‘hello world’ moment we’ve been waiting for the most meaningful milestone to date in the quest to make quantum computing a reality.”
“This demonstration of quantum supremacy over today’s leading classical algorithms on the world’s leading supercomputers is truly a remarkable achievement,” William Oliver, a computer researcher at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology, wrote in a comment piece on the discovery.
“This experiment establishes that today’s quantum computers can outperform the best conventional computing for a synthetic benchmark,” says Travis Humble, the director of Oak Ridge’s Quantum Computing Institute.
In this research along with Google, NASA, and the Oak Ridge National Laboratory were also included.
Photo: Ryan F. Mandelbaum
On the other side of the competition, IBM one of the major players in Quantum Computing is not ready to believe in Google’s results and has pointed out many questions on the research.
IBM has claimed that the traditional supercomputer used in Google’s experiment (IBM’s own Summit machine), wasn’t utilized efficiently, which they say explains the less-than-flattering 10,000-year time lag.
By calibrating Summit differently for the same experiment, IBM argues “an ideal simulation of the same task can be performed on a classical system in 2.5 days and with far greater fidelity” and the researchers have published both a blog post and a working paper to make their case.
“While we believe that some quantum computations will be out of reach of any conventional computer, it is a challenge to argue that any particular set of processes cannot be simulated through some suitable trick,” quantum information theorist Stephen Bartlett from the University of Sydney told ScienceAlert last month.
“I suspect that the first claims of quantum supremacy will be followed by a lengthy period of contention, where scientists push the limits of conventional supercomputers to find a way to simulate these claimed demonstrations,” he added.
“It is likely that the classical simulation time, currently estimated at 10,000 years, will be reduced by improved classical hardware and algorithms, but, since we are currently 1.5 trillion times faster, we feel comfortable laying claim to this achievement,” says one of the group, Brooks Foxen from UC Santa Barbara.
In return to IBM’s and other researchers’ questions, Google’s lead researcher John Martinis said IBM’s initial retort remained hypothetical and had to be substantiated.
“We’re looking forward to when people actually run the idea on Summit and check it and check our data because that’s part of the scientific process – not just proposing it but actually running it and checking it,” Martinis said.
More in AI
World’s First Artificial Intelligence University Opens in Abu Dhabi UAE
The Start Of AI Killing Jobs Of Models, Here Are 100,000 Free AI-generated Potentiates
Facebook Selects 6 Projects From India For AI Ethics Research Awards
MIT Creates World’s First Psychopath AI By Feeding It Reddit Violent Content
Elon Musk’s AI project to replicate the human brain receives $1 billion from Microsoft
- ← World’s First Artificial Intelligence University Opens in Abu Dhabi UAE
- Shake Your Booty: AI Deepfakes Dance Moves From a Single Picture →
You May Also Like

Japanese Researchers Build An AI That Identifies Early-Stage Of Stomach Cancer

The New AI System That Could Replace Your Baseball Umpire Soon

The New AI Toilets Will Scan Your Poop To Diagnose Your Ailments
News

Deep Learning Pioneers Yann LeCun and Yoshua Bengio Elected as AAAI-20 Fellows
- 377Shares
The world’s one of most renowned association of AI, the AAAI or Association for the Advancement of Artificial Intelligence has

Intel Acquires Israel-Based AI Chipmaker Habana Labs for $2 billion

AI Has Been Introduced As A Subject In CBSE Classes & IBM Will Design The Curriculum

Amazon Launch Quantum Cloud Computing Service Called Braket Into AWS

The DeepMind CEO & Co-Founder Is Joining Google As The AI Lab Positions

This AI System Allows A Paralyzed Person To ‘Handwrite’ Using His Mind

An App Called ThirdLove Using AI To Find Correct Bra Size

Jio Institute Offering Undergraduate Courses in AI & Data Science From 2021
About Us
Hii! This is Navin
Techgrabyte is an education website whose area of work is Artificial Intelligence, Machine Learning and Deep Learning.
Join our Newsletter, to get daily update.
“AI is the new electricity”
About UsCOPYRIGHT © 2020 TechgraByte | All RIGHT RESERVED BY NAVIN BONDADE×Get Notifications
All articlesExplorePCR technology
Role of DMSO in PCR: DMSO a PCR enhancer
05/10/2018 0 Comments
The role of DMSO in PCR amplification is to increase the specificity and yield of PCR. DMSO is a PCR enhancer which is an important ingredient of PCR buffer. In this article, we will discuss the structure and function of DMSO and how we can utilize DMSO for enhancing the PCR reaction and finally, my ultimate guide for using DMSO.
The PCR buffer is used to enhance a PCR reaction made up of MgCl2, KCl, albumin, (NH4)2 SO4 and DMSO. However, the manufacturer never reveals the exact concentration and component of their buffer.
Each of the listed components is specifically utilized to perform a specific function. For example, the MgC2 work as the cofactor of Taq DNA polymerase. For more detail on MgCl2 and Taq DNA polymerase please read our articles:
Function of taq DNA polymerase in PCR
Structure of DMSO
DMSO, Dimethyl sulfoxide is an organic solvent molecule. As shown in the figure, it has the trigonal pyramidal symmetry. The unique solvent and melting properties of DMSO makes it unique above all organic compounds and hence it is applicable in molecular biology and as a Cryoprotectant in medicinal research. Several properties of DMSO are listed here,

The image represents the structure of Dimethyl sulfoxide having two methyl group with pyramidal symmetry.
Properties of DMSO
- It is a polar solvent and dissolves in both, polar and non-polar solutions.
- It has a higher melting and boiling point.
- The dielectric constant of DMSO is ~ 48. 9.
- The pKa value is 35.1
Interestingly, not everyone is familiar with the DMSO and how to use DMSO in PCR because it is used in some special type of PCR reactions. One of the special types of PCR reaction is high GC rich PCR.
GC content of templet DNA is one of the causes of failure in PCR reaction. The high GC content results in reaction failure, non-specific bindings or non-confirmative results.
The DNA is made up of A, T, G and C. Two hydrogen bond between A and T and three hydrogen bond between G and C are present. The triple hydrogen bond between G and C makes them more stable during PCR. The high temperature is required to break the triple bonds between G and C and due to higher stability, it leads to secondary structure formation during PCR.
Additionally, it causes a non-specific binding of primer results in the non-confirmative result. To overcome these problems, DMSO is added to the PCR buffer.
[wp_ad_camp_1]
Role of DMSO in PCR
DMSO makes GC rich DNA more heat labile and reduces the Tm of reaction. Here, DMSO directly binds to the Cystine residue of the GC rich region and changes the conformation of Cystine which makes it more heat labile.
Hypothetically, DMSO reduces the strength of the hydrogen bond between the major and the minor groove of DNA. The DNA structure becomes unstable which decreases the denaturation temperature.
DMSO even prevents the secondary structure formation. Due to the high GC content in DNA, the DNA creates the secondary structure or hairpin loop. Three hydrogen bond require more energy to broke, the secondary structure is formed by binding of single-stranded DNA with each other, just like a hairpin loop.

Image credit: http://www.memorangapp.com
The image represents how the single-stranded DNA creates DNA hairpin-like structure.
This will result in PCR failure. DMSO binds to the DNA and prevents the reannealing of single-stranded DNA. It also facilitates the annealing of primer with templet. Therefore, it increases the specificity and yield of PCR reaction.
Generally, the GC content of the PCR is between 45% to 52%. If the GC content is higher than the desired range use 5% DMSO in PCR reaction. 4% to 10% DMSO concentration can be utilized to optimize the PCR reaction.
Further, it depends on the type of reaction, the GC content of DNA and the quality of DMSO.
Beside increasing specificity, it changes the DNA topology as well. DMSO releases supercoiling of DNA which is confirmed by plasmid studies. Here, DMSO greatly induces the activity of topoisomerase I. The topoisomerases are the enzyme which helps in relaxing the DNA.
Therefore, it boosts the reaction specificity by relaxing the negatively supercoiled DNA. However, DMSO is already present in the PCR buffer but still, we can use extra DMSO if amplification is not obtained (mainly in high GC rich DNA).
Besides use in molecular genetics, it is even applicable in cell proliferation, inhibition and differentiation studies and as a crypto preservative as well.
Apart from these advantages, DMSO has one major disadvantage. Boosting PCR amplification is not always useful, as it increases the mispairing of bases. This will induce mutagenesis.
The DMSO incorporates mutations in the amplicon by mismatch base pairing. An inappropriate amount of DMSO facilitates the flexibility to primer templet binding, the activity of Taq polymerase is greatly increased results in mismatch base-pairing. Hence the rate of mutation is increased by increasing the concentration of DMSO.
So what is the exact concentration of DMSO for PCR reaction?
My ultimate guide for using DMSO in PCR
Based on the available research data, you have to optimize your own reaction. Don’t worry I will tell you how
If the GC content of your DNA is ~60% use exactly 5% of DMSO. More detail on the effect of GC content and how to check the GC content of DNA please read our article, PCR primer design guidelines
If the GC content is more than 60%, it is considered as a highly sensitive reaction, for optimizing this reaction, you have to optimize the PCR by adding three of four types of different combination of DMSO. Ideally, use 5.5%, 6% or 7% of DMSO in three different reactions.
Analyse the result and decide which combination is good for your reaction. Interestingly, you can use DMSO artistically. We are a scientist but we are also an artist. We can run more than 2 reactions on the same annealing temperature.
Addition of DMSO decreases the annealing temperature of the PCR reaction. So if you have two reactions at once. For example, one with annealing temperate of 60°C and other with 63°C by adding DMSO to the reaction of 63°C temperature we can reduce the annealing temperature of that reaction and ultimately, we can run both reactions at the same annealing temperature of 60°C.

Image credit: http://www.thermofisher.com
The image represents the results of DMSO enhanced PCR reaction. As shown in the figure the best result observed with 9% DMSO. The DNA for this reaction has 76% GC content. if the GC content is nearly 60%, then 4.5% DMSO will give the best result.
However, for doing this, you need to have expertized and special skills regarding PCR. You have to perform so many experiments at once for mastering these types of skill. Once you know about each and every component used in PCR, you can do it easily.
Therefore, our motto of writing these types of content is to give you expertize theoretically through our personal research experience. If you have any question regarding the topic or want or know more please comment in the comment box.
Article covered by: Tushar Chauhan
Article reviewed by: Ravi Parmar
[wp_ad_camp_2]
Share this:
What are the different components used in the PCR reaction buffer?
PCR reaction: Ten secrets that nobody tells you
Share Article:
Tags:
Dimethyl sulfoxideDMSO a PCR enhancerDNA hairpinRole of DMSO
Dr Tushar Chauhan
02/10/2018
Function Of Taq DNA Polymerase In PCR

07/10/2018
The XX chromosome in male: A case of sex reversal

Leave a Reply
Our ebook
Buy our eBook “From DNA extraction to PCR” from here:
Subscribe to Blog via Email
Enter your email address to subscribe to this blog and receive notifications of new posts by email.
Email Address
Subscribe
Categories
Select Category All articles Behavioural genetics Books Chromosomes Cytogenetics DNA DNA Extraction DNA fingerprinting DNA packaging DNA sequencing DNA topology Educational articles Epigenetics Explore Extrachromosomal inheritance Gel electrophoresis Gene therapy Genetic Engineering Genetic Test Genome Immunogenetics Mutation PCR technology Real-time PCR Replication Reviews RNA RNA Transposons Select Category
- Select Category
- All articles
- Behavioural genetics
- Books
- Chromosomes
- Cytogenetics
- DNA
- DNA Extraction
- DNA fingerprinting
- DNA packaging
- DNA sequencing
- DNA topology
- Educational articles
- Epigenetics
- Explore
- Extrachromosomal inheritance
- Gel electrophoresis
- Gene therapy
- Genetic Engineering
- Genetic Test
- Genome
- Immunogenetics
- Mutation
- PCR technology
- Real-time PCR
- Replication
- Reviews
- RNA
- RNA
- Transposons
PCR Types:
Recent Posts
- Differences Between Probe Vs Primer
- Nucleotides Vs Nucleosides
- DNA Probes: Labelling, Types And Uses
- What Is DNA Methylation?
- “Transcription And Translation” A Brief Overview
Interesting Reads:
DNA polymerase vs RNA polymerase
Disclosure
This website contains affiliate links inside the article.
Subscribe to Blog via Email
Enter your email address to subscribe to this blog and receive notifications of new posts by email.
Email Address
Subscribe
Archives
Select Month December 2019 November 2019 October 2019 September 2019 August 2019 July 2019 June 2019 May 2019 April 2019 March 2019 February 2019 January 2019 December 2018 November 2018 October 2018 September 2018 August 2018 July 2018 June 2018 May 2018 Select Month
- Select Month
- December 2019
- November 2019
- October 2019
- September 2019
- August 2019
- July 2019
- June 2019
- May 2019
- April 2019
- March 2019
- February 2019
- January 2019
- December 2018
- November 2018
- October 2018
- September 2018
- August 2018
- July 2018
- June 2018
- May 2018
Genetic Education
© 2018 Genetic Education Inc. All rights reserved.

Top 6 Most Amazing Ways 3D Printing Is Now Used In Practice

Future Of Work
The way we manage, lead and work in modern organisations is evolving and changing constantly.
Série Semanal
50609 assinantesAssinar
Top 6 Most Amazing Ways 3D Printing Is Now Used In Practice
Published on 2019 M12 22

Bernard MarrFollow
Internationally best-selling author, keynote speaker, futurist, and strategic business & technology advisor
84232
- 0
Even though 3D printing got its start in the 1980s when Chuck Hull designed and printed a small cup, it’s been in the last few years that the printers became cheaper to produce and therefore used in a variety of amazing ways. Also known as additive manufacturing, 3D printing is when objects are created when a printer lays down material in successive layers following the design from a digital file. Here are the top 6 most amazing ways 3D printing is now used in practice today.
1. Manufacturing
3D printing is reshaping the way we manufacture things in a wide range of industries. Thanks to innovations with 3D printing technology, materials, and equipment, costs have gone down, making it easier to be adopted for general manufacturing. 3D printing allows manufacturers to consider short-production runs and to create completely new components that wouldn’t be feasible in a traditional manufacturing environment. Manufacturers are also able to be nimble when they use 3D printing processes. McLaren Racing provides a great example of how 3D printing can impact an industry. They use 3D printing to develop steering wheels for their Formula One racing cars. Since they can print a wheel and allow drivers to handle various prototypes and offer feedback, the design process went much quicker than with traditional design and manufacturing processes. 3D printing is used to rapidly develop and create new parts and tools—even at the racetrack—that will hopefully enhance the performance of the cars.
2. Edible 3D printing
Who doesn’t like chocolate? One of the ways 3D printing is used today is to create objects out of edible material such as chocolate. Since chocolate hardens quickly at room temperature, it’s the perfect material for 3D printing and allows chocolatiers to create confections in any shape or form. This use of 3D printing will only get bigger as other edible materials are used, including ice cream, cookie dough, pizza, and even hamburger to make patties. Edible 3D printing is becoming popular for professionals and for personal use. Those that use 3D printers for edible creations find that it can be less time-consuming than traditional cooking, allows for more personalization and customization, and there’s no limit to creativity.
3. Musical instruments
The world has already experienced its first live concert, where only 3D-printed instruments were used at Lund University in Sweden. 3D printing enables instruments and instrument parts to be created in complex shapes that aren’t possible in any other way. So far, there have been violins, flutes, keyboards, guitars, and drums created by 3D printing. While the craft of building a violin hasn’t changed since the 17th century, 3D printing offers another solution. Many 3D-printed instruments not only make beautiful music, but are visually stunning as well.
4. Dresses
3D printing in the world of fashion? Yes, it’s the next 3D printing frontier! Nike already has the capability to create trainers using 3D printing, but now designers are relying on the technology to create amazing dresses that couldn’t be fabricated in any other way. With 3D printing, fashion fuses with technology and the normal fashion rules do not apply.
5. Entire houses
Within 24 hours, an entire 400-square-foot house was 3D printed in the suburbs of Moscow for only $10,000. In the last several years, other construction companies have put this technology of 3D printing concrete to use and made the price to create a 3D printed house drop as well. And the most advanced 3D printed building in the world is a futuristic office building in Dubai. The speed of construction for a 3D home is especially appealing when emergency shelters must be erected after natural or manmade disasters. Aside from expediency, 3D printing houses allow for unlimited creative opportunities that weren’t possible in traditional construction.
6. Print body parts
One of the most amazing real-world examples of 3D printing is the technology’s use in healthcare and medicine. From bone structures that can be implanted in the human body to organs and heart and liver tissue, 3D printing is going to transform medicine and the future of mankind. These aren’t just prototypes; in many cases, these are actual working body parts. The medical school at Northwestern University even 3D printed ovaries for mice and allowed infertile mice to produce healthy offspring.
Thank you for reading my post. Here at LinkedIn and at Forbes I regularly write about management and technology trends. I have also written a new book about AI, click here for more information. To read my future posts simply join my network here or click ‘Follow’. Also feel free to connect with me via Twitter, Facebook, Instagram, Slideshare or YouTube.
About Bernard Marr
Bernard Marr is an internationally best-selling author, popular keynote speaker, futurist, and a strategic business & technology advisor to governments and companies. He helps organisations improve their business performance, use data more intelligently, and understand the implications of new technologies such as artificial intelligence, big data, blockchains, and the Internet of Things.
LinkedIn has ranked Bernard as one of the world’s top 5 business influencers. He is a frequent contributor to the World Economic Forum and writes a regular column for Forbes. Every day Bernard actively engages his 1.5 million social media followers and shares content that reaches millions of readers.
Publicado por

Bernard Marr
Internationally best-selling author, keynote speaker, futurist, and strategic business & technology advisor
Top 6 Most Amazing Ways 3D Printing Is Now Used In Practice #3D #printing is no longer just a futuristic concept; it’s being used in a variety of amazing ways today. From changing the face of what’s possible in #manufacturing to building human body parts and #organs that will #transform #healthcare and #medicine, here are 6 of the best real-world examples of #3DPrinting.32 comments

Sign in to leave your comment

Beth Hill-Skinner
KEYNOTE SPEAKER / GLOBAL AFFAIRS CONSULTANT- Resource For Understanding U.S. & Geopolitical Events
Crazy to see a heart printed with a 3D machine22 hGosteiResponder

Usuário do LinkedIn
Great Insights….3 dGosteiResponder1 gostou

Ella Marushchenko
scientific illustrator at Ella Maru Studio
which materials can be used with 3d printing in a lab?3 dGosteiResponder

Deborah Graves
Human Resources Recruiter at CareAparent™
My husband and I just donated brand new 3D printer, and software to private school’s innovation dept. The student are loving it and putting it to good use. Smart kids and their projects are just amazing.3 dGosteiResponder5 gostaram2 respostas
Dimitrios Pletsas
Senior fund development officer, College of Engineering, Swansea University
This sounds great! Similar experience here in Wales: started with 1 printer and then 7 more on loan from my work (Swansea University). Then each school printed a RC race car and had a race: https://www.swanseabaycitydeal.wales/news/top-gear-for-pupils-at-3d-printed-car-race/3 dGosteiResponder2 gostaram
Ivan Campos
Técnico em contabilidade at E E P S G Dr. Alarico da Silveira
I am very happy with people like you, sharing possibilities for the development of new generations.3 dGosteiResponder1 gostou
Bård Steen Hansen
Gleder meg til å starte Thomas Aanstad Evensen med dette.Ser utrolig mange muligheter😀3 dGosteiResponder2 gostaramShow more comments.
Mais de Bernard Marr
The 10 Best Examples Of How Companies Use…
2019 M12 17
What Is The Internet Of Bodies (IoB)? And…
2019 M12 15
7 Unmissable Innovations And The Latest…
2019 M12 10
- © 2019
- Sobre nós
- Contrato do Usuário
- Política de Privacidade do LinkedIn
- Política de Cookies
- Política de Direitos Autorais
- Política da Marca
- Controles de visitantes
- Diretrizes da Comunidade



Like!! Great article post.Really thank you! Really Cool.
LikeLike
Thank you ever so for you article post.
LikeLike
These are actually great ideas in concerning blogging.
LikeLike
Hey there! Someone in my Facebook group shared this site with us so I came to give it a look. I’m definitely loving the information. I’m book-marking and will be tweeting this to my followers! Great blog and outstanding design.
LikeLike
I like this website very much, Its a very nice office to read and incur information.
LikeLike